7th June 2024 (13 Topics)
Context
The world is facing a major debt crisis, hindering progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030. Global debt, including loans taken by households, businesses, and governments, has soared to USD 315 trillion in 2024, three times the global GDP, as per a UN Report.
Key Points:
- Report Title: A world of debt 2024: A growing burden to global prosperity
- Unmanageable Debt Levels: The amount of debt per person would be around USD 39,000 if divided among the world's population. Debt servicing, especially interest payments, consumes a significant portion of revenues, limiting funds available for crucial sectors like health and education.
- Types of Debt: Household debt is at USD 59.1 trillion, business debt at USD 164.5 trillion, and public debt at USD 91.4 trillion. This level of debt is comparable to historical highs seen during events like the Napoleonic Wars.
- Changing Aid Dynamics: Development aid has decreased, with concessional loans replacing aid, adding to developing countries' debt burden. Additionally, support to reduce debt among developing countries has declined significantly.
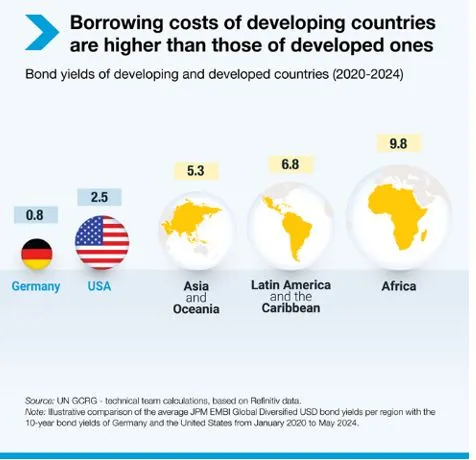
- In 2023, developing nations paid USD 847 billion in net interest, a 26% increase from 2021. They borrowed internationally at rates two to four times higher than the U.S. and six to 12 times higher than Germany.
What are the impacts?
- Risks and Consequences: Countries risk defaulting on debt if they can't repay it, leading to budget cuts in vital development programs.
- For example, African countries are spending a significant portion of government funds on debt interest payments, impacting education and health spending.
- Impact on Development: High public debt restricts spending on development sectors, particularly in developing and poor countries. Developing countries, which account for 30% of global debt, are experiencing a faster rate of debt growth compared to developed nations.
- Impact on SDGs: High debt levels are a major obstacle to achieving SDGs, as countries struggle to allocate resources towards sustainable development initiatives.
Required Measures
The report suggests a plan to overhaul the global financial system and enhance the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) stimulus package to address the current debt crisis. This involves:
- Improving Developing Countries' Participation: Ensure developing countries have a stronger say in global financial system governance to better represent their interests.
- Addressing Debt Challenges: Implement an effective mechanism to handle increasing debt costs and prevent countries from falling into severe debt situations.
- Boosting Liquidity: Provide more contingency finance to offer greater financial stability during crises, reducing the need for countries to resort to additional borrowing.
- Expanding Access to Financing: Increase access to affordable, long-term financing by mobilizing resources from multilateral development banks and private sectors on a large scale.
More Articles