7th June 2024 (13 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
Fifty-seven years have passed since the Six-Day War, fought between Israel and its Arab neighbours between June 5 and June 10, 1967.
Key-details of the War
- Roots of the Conflict: The Six-Day War, fought between Israel and its Arab neighbors in June 1967, stemmed from long-standing tensions over territorial and water disputes.
- The establishment of Israel led to a refugee crisis among Palestinian Arabs, fueling animosity with neighboring Arab states, particularly Egypt under President Nasser.
- Outbreak of the War: The conflict was triggered by Egypt's naval blockade of the Straits of Tiran, vital for Israeli commerce.
- Israel, feeling threatened, launched a pre-emptive strike against Egyptian airfields on June 5, 1967.
- This swiftly escalated into a full-scale war as Jordan and Syria joined the conflict.
- Israeli Victory and Consequences: Israel emerged victorious, gaining control of significant territories, including the Sinai Peninsula, Gaza, the Golan Heights, the West Bank, and East Jerusalem.
- The defeat humiliated the Arab nations and established Israel's dominance in the region.
- The war also spurred Palestinian nationalism and led to the formation of the PLO.
- Long-Term Implications: The Six-Day War reshaped the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East and fueled ongoing tensions.
- Israel's occupation of East Jerusalem, the West Bank, and Gaza remains a contentious issue, with the fate of Palestinian refugees from the conflict unresolved.
- Subsequent conflicts, like the 1973 Yom Kippur War, reflect attempts to reverse the Arab losses of the Six-Day War.


Mains Issues
Context
Denmark, Greece, Pakistan, Panama, and Somalia have been recently elected to serve on the U.N. Security Council for two-year terms. In recent times, countries are advocating for reforms within the UNSC to ensure equitable representation and effectiveness in addressing global security challenges.
Key-highlights
- The Security Council consists of 15 members, including five permanent members with veto power and ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- Selection Process: Members are chosen through a voting process where nominees from regional groupings are voted on by all 193 U.N. member states.
- Regional Representation: This year's selections include Somalia for Africa, Pakistan for Asia-Pacific, Panama for Latin America and the Caribbean, and Denmark and Greece for two Western seats.
Why UNSC requires “reforms”?
- The formation of the UN Security Council, comprising five permanent members — China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States — occurred nearly eight decades ago.
- At that time, the global landscape comprised approximately 50 independent nations.
- Despite the significant increase in the number of sovereign states to around 193 today, the control over UNSC membership has remained concentrated in the hands of the original five permanent members.
- India's Efforts: India, alongside Japan, Germany, and Egypt, has actively advocated for UNSC reform. The proposal put forth by this coalition seeks to address the imbalance in representation and enhance the Council's effectiveness.
- Challenges Faced: Obtaining consensus for UNSC reform has proven challenging. While some nations have expressed support, others have been hesitant or resistant to change. Overcoming these hurdles necessitates concerted efforts and strategic diplomacy.
Global Support for India's Candidacy:
- India's aspiration for a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) has been a longstanding diplomatic endeavour.
- India's rising global stature and widespread support from various regions position it favorably for a permanent seat on the UNSC. India's economic growth, large population, vibrant democracy, and diplomatic prowess under Prime Minister Modi's leadership provide a strong foundation for garnering support.
- Support from the African Union, ASEAN nations, the United States, European countries, and other regions underscores India's candidacy.
- Potential Opposition: While China remains a potential obstacle to India's permanent membership, diplomatic efforts could sway opinions, especially if China stands isolated in its opposition.
About UNSC
|


Mains Issues
Context
After the recent Lok Sabha Election 2024, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh are demanding special category status for their respective states. However, the Fourteenth Finance Commission removed the concept of special category status from states, and since then, the Centre has largely discouraged calls for special category status in recent years.
What is Special Category Status?
- Special Category Status (SCS) is a classification granted by the Centre to certain states in India to aid in their development.
- It is based on specific geographical and socio-economic disadvantages. The scheme was introduced in 1969 following recommendations from the Fifth Finance Commission.
- Criteria for Granting SCS: Before granting SCS to a state, five factors are considered:
- Hilly and difficult terrain
- Low population density and/or significant tribal population
- Strategic location along international borders
- Economic and infrastructural backwardness
- Non-viable nature of state finances
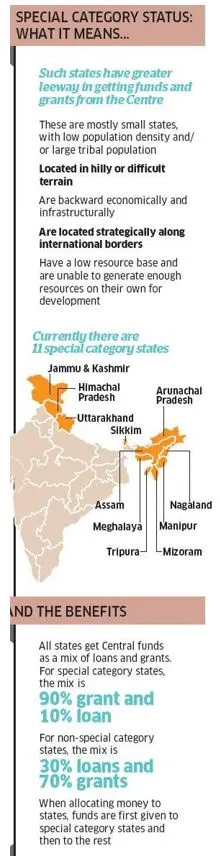
- Currently, 11 states in India have been granted SCS, including Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, and Uttarakhand.
- Benefits of SCS:
- States with SCS receive funding from centrally sponsored schemes in a more favorable ratio of 90:10 (Centre), compared to general category states. For Non-Special Category Status, the Normal Central Assistance was calculated as 30% grant and 70% loan.
- They are provided Special Plan Assistance for projects of special importance to the state.
- Unspent funds do not lapse at the end of the financial year.
- They also enjoy other benefits such as tax concessions.
Why Bihar is Demanding SCS?
- Bihar is demanding SCS due to its low per capita net state domestic product and high poverty rates.
- Its per capita income is among the lowest in the country, and a significant portion of its population is multidimensionally poor according to the National Family Health Survey 5.
Why Andhra Pradesh is Demanding SCS:
- Andhra Pradesh is seeking SCS primarily because of the revenue loss it experienced after the 2014 bifurcation of the state, which led to the formation of Telangana.


Mains Issues
Context
The 2024 Lok Sabha election results led to a sharp decline in the Indian stock market. This highlights the market's sensitivity to both big-picture (macroeconomic) and specific (microeconomic) factors, including global economic trends, individual company performance, and international investor behavior. As India's market becomes more globalized, changes in Indian indexes now have ripple effects on global markets.
Impact of Global Indices
- GIFT Nifty: The shift from SGX Nifty to GIFT Nifty aims to better regulate Nifty derivatives trading. This change is part of India's efforts to enhance its financial sector and attract global investors to its designated international finance center.
- Impact of GIFT Nifty:
- GIFT Nifty connects with the NSE Nifty, allowing for real-time price reactions.
- It provides more ways to access Indian stocks, potentially increasing trading activity.
- It serves as a benchmark for the Indian market, even when the market is closed.
- Overall, it's seen as a positive addition to the market, despite still evolving.
- Indian VIX: The Indian VIX, also known as the Fear Index, measures how much investors worry about market uncertainty. A high VIX suggests more volatility, while a low VIX means investors are more confident.
- Impact of Indian VIX:
- It shows how risky investors think the market is.
- A sudden increase in VIX means investors expect more ups and downs.
- It tends to move opposite to the Nifty index.
- When the VIX is at its highest, it could signal a good time to buy stocks.
- NASDAQ: The NASDAQ stock exchange, known for its focus on tech companies, can affect the Indian market. Changes in NASDAQ can influence global investor attitudes toward tech stocks, which impacts confidence worldwide.
- Impact of NASDAQ:
- Foreign investment in NASDAQ indirectly affects Indian markets.
- Investments crossing borders can affect Indian companies listed on NASDAQ.
- Various factors, including domestic conditions and global trends, affect Indian markets.
- FTSE 100: The UK's FTSE 100 index influences the Indian market due to global investment connections. Changes in the FTSE 100 can affect how investors feel about investing in India.
- Impact of FTSE 100:
- Uncertainty in the UK, like Brexit, can affect the FTSE 100.
- Investors may look to India for growth opportunities.
- A drop in the FTSE 100 could lead to more investment in India.
- A strong FTSE 100 boosts investor confidence worldwide, benefiting Indian equities indirectly.
- Brent Crude Oil: Global oil prices, specifically Brent Crude, can affect stock markets, including India's. Changes in oil prices impact company profits and investor confidence.
- Impact of Brent Crude Oil:
- Rising oil prices can hurt company profits and stock prices.
- Falling oil prices can boost investor confidence and stock prices.
- Recent events, like the virus outbreak, show that oil prices may not always have a big impact on stock markets.
Fact Box: Working of Indian Stock Market
|


Mains Issues
Context
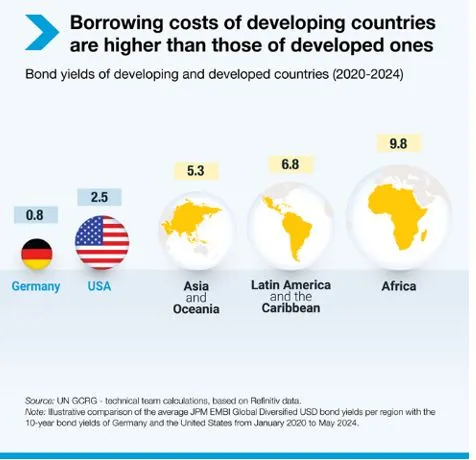
The world is facing a major debt crisis, hindering progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030. Global debt, including loans taken by households, businesses, and governments, has soared to USD 315 trillion in 2024, three times the global GDP, as per a UN Report.
Key Points:
- Report Title: A world of debt 2024: A growing burden to global prosperity
- Unmanageable Debt Levels: The amount of debt per person would be around USD 39,000 if divided among the world's population. Debt servicing, especially interest payments, consumes a significant portion of revenues, limiting funds available for crucial sectors like health and education.
- Types of Debt: Household debt is at USD 59.1 trillion, business debt at USD 164.5 trillion, and public debt at USD 91.4 trillion. This level of debt is comparable to historical highs seen during events like the Napoleonic Wars.
- Changing Aid Dynamics: Development aid has decreased, with concessional loans replacing aid, adding to developing countries' debt burden. Additionally, support to reduce debt among developing countries has declined significantly.
- In 2023, developing nations paid USD 847 billion in net interest, a 26% increase from 2021. They borrowed internationally at rates two to four times higher than the U.S. and six to 12 times higher than Germany.
What are the impacts?
- Risks and Consequences: Countries risk defaulting on debt if they can't repay it, leading to budget cuts in vital development programs.
- For example, African countries are spending a significant portion of government funds on debt interest payments, impacting education and health spending.
- Impact on Development: High public debt restricts spending on development sectors, particularly in developing and poor countries. Developing countries, which account for 30% of global debt, are experiencing a faster rate of debt growth compared to developed nations.
- Impact on SDGs: High debt levels are a major obstacle to achieving SDGs, as countries struggle to allocate resources towards sustainable development initiatives.
Required Measures
The report suggests a plan to overhaul the global financial system and enhance the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) stimulus package to address the current debt crisis. This involves:
- Improving Developing Countries' Participation: Ensure developing countries have a stronger say in global financial system governance to better represent their interests.
- Addressing Debt Challenges: Implement an effective mechanism to handle increasing debt costs and prevent countries from falling into severe debt situations.
- Boosting Liquidity: Provide more contingency finance to offer greater financial stability during crises, reducing the need for countries to resort to additional borrowing.
- Expanding Access to Financing: Increase access to affordable, long-term financing by mobilizing resources from multilateral development banks and private sectors on a large scale.


Prelims Articles
Context
Pakistan’s Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif is visiting China because China is Pakistan’s biggest ally, and they're expected to announce the second phase of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
What is the CPEC and why is it significant?
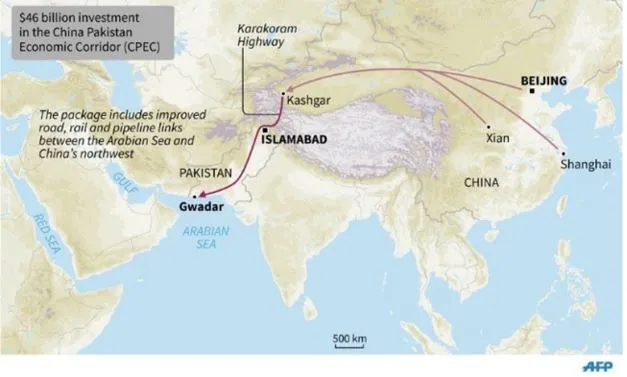
- The CPEC is a $62-billion project started in 2015 by China to invest in infrastructure projects in Pakistan.
- Objective: to connect China's Xinjiang region with Pakistan's Gwadar and Karachi ports.
- It is part of China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- It's important because it helps China expand its influence and gives it direct access to the Indian Ocean through Pakistan.
- First phase of CPEC: In the first phase, some power projects and transport projects were completed, but progress has been slow overall, with many projects not yet started or completed.
Controversies surrounding CPEC
- Ecological and Human Security Concerns: Since 2015, people are worried about how CPEC could harm Balochistan's environment and the safety of its residents.
- Debt Trap Allegations: Some say CPEC might trap Pakistan in debt, and they doubt if the benefits are fairly shared.
- Security Issues: Attacks on Chinese workers by local groups have strained China-Pakistan relations.
- Indian Opposition: India stands against the CPEC, citing concerns over its impact on India's territorial integrity and sovereignty.


Prelims Articles
Context
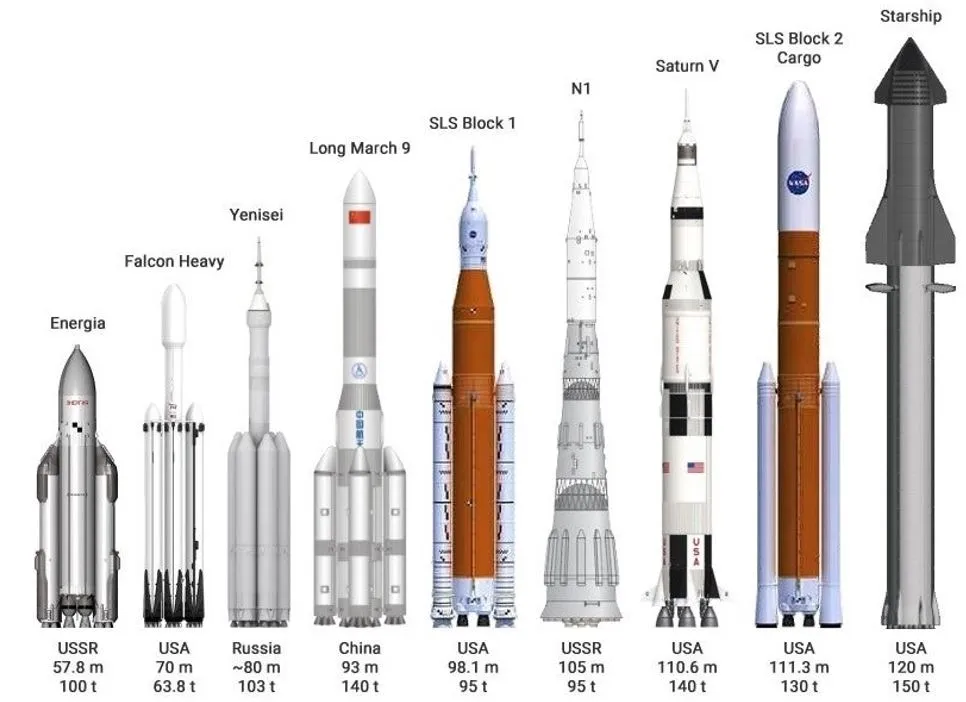
SpaceX successfully completed the fourth test flight of its Starship rocket, marking a significant advancement in rocket technology. The 400-foot-tall Starship rocket was launched atop a thundering pillar of fire.
Key-highlights:
- The main objectives were to bring down Starship's first-stage booster, known as Super Heavy, for a soft splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico.
- Additionally, the goal was to achieve a controlled reentry of the 165-foot-tall upper stage, called Starship or Ship.
- Both the Super Heavy booster and the Ship successfully made water landings, eliciting cheers from spectators at SpaceX's mission control at Starbase.
Significance of Starship:
- The Starship system is designed to be fully reusable and aims to revolutionize space travel by ferrying cargo and people beyond Earth.
- It is critical to NASA's plan to return astronauts to the moon, with SpaceX winning a multibillion-dollar contract from the agency to use Starship as a crewed lunar lander as part of the Artemis moon program.
Fact Box: About Starship:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
UK scientists have identified a significant genetic weakness present in 95% of people with IBD. This weakness makes certain immune cells, particularly macrophages, more prone to triggering excessive inflammation in the bowels.
Key Findings:
- Role of Macrophages: Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in IBD by releasing inflammatory chemicals called cytokines in the intestines. Excessive inflammation caused by macrophages is a key characteristic of IBD.
- Master Regulator Gene: Through deep genetic analysis, researchers discovered a specific section of DNA that acts as the "master regulator" for inflammation in macrophages. Individuals with a particular version of this gene are more susceptible to developing IBD due to their heightened inflammatory response.
- Potential Treatment Avenue: Drugs already approved for other conditions, such as cancer, have shown promise in reducing inflammation in IBD patients' samples. These drugs target the problematic macrophages and could potentially serve as a treatment for IBD in the future.
Fact Box: About Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
India's high net-worth individuals (HNWI) experienced significant growth in both population and wealth, driven by favorable market conditions and economic indicators. This trend aligns with the broader global increase in HNWI wealth and population observed in 2023, as per The Capgemini Research Institute’s World Wealth Report 2024.
Key-highlights:
- Increase in HNWI Population and Wealth:
- In 2023, India saw a significant rise of 12.2% in the number of high net-worth individuals (HNWI), reaching a total of 3.589 million.
- The financial wealth of India's HNWIs also increased by 12.4% to $1,445.7 billion, compared to $1,286.7 billion in 2022.
- This growth was attributed to market buoyancy, which spurred a $3.8 trillion increase in HNWI wealth globally.
- Performance in the APAC Region:
- India and Australia were among the top performers in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region.
- India recorded a 12.4% growth in HNWI wealth and a 12.2% increase in HNWI population, driven by a resilient economy and strong performance in equity markets.
- Economic Indicators:
- India's unemployment rate decreased to 3.1% in 2023 from 7% in 2022, despite a 7.3% growth in the economy.
- Market capitalization in India increased by 29.0% in 2023, reflecting a robust equity market.
- National savings as a percentage of GDP also rose to 33.4% in 2023, up from 29.9% in 2022.
Global Trends:
- Globally, HNWI wealth and population increased by 4.7% and 5.1% respectively in 2023.
- This growth was supported by a resurging equity market and improving macroeconomics.


Prelims Articles
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Global debt |
Global debt is borrowing by governments, businesses and people, |
|
2. |
Macrophages |
Macrophages are a type of white blood cell that play an integral part in the immune system. They help eliminate foreign substances by engulfing foreign materials and initiating immune responses. |
|
3. |
Market Capitalisation |
Market cap is the total value of a company's stock, found by multiplying the stock price by the number of outstanding shares. |
|
4. |
Special Category Status (SCS) |
Special Category Status (SCS) is allotted to state to amplify its growth if they are backward. The status is awarded to their growth rate if they face geographical and socio-economic disadvantages. |


Editorials
Context
The integration of AI with molecular biology has led to groundbreaking advancements, particularly in the understanding and manipulation of proteins. This has opened up new possibilities for disease treatment and personalized medicine.
AI’s Role in Understanding Proteins:
- Introduction to the Issue:Proteins, the building blocks of life, have diverse roles in biological functions. Understanding their structure, particularly how they fold, is crucial for medical science. AI has made significant strides in this area, with Google DeepMind’s AlphaFold predicting protein folding with remarkable accuracy.
- Significance of Protein Folding:Misfolded proteins can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. With over 200 million known proteins, each folding in a unique three-dimensional shape, studying each one was previously impossible. AlphaFold’s ability to predict protein folding could revolutionize our approach to disease treatment.
- AI’s Impact on Medical Science:The success of AlphaFold is considered a breakthrough on par with mapping the human genome or the discovery of antibiotics. It has the potential to change medical science forever.
AI’s Contribution to Protein Design and Gene Editing:
- Generative AI in Protein Design:New AI technologies like LLMs and Generative AI are being used to generate blueprints for new proteins. These proteins could revolutionize our ability to combat diseases. For instance, GenAI can create proteins of a unique shape, such as the spike protein of the COVID virus.
- AI in Gene Editing:AI is also making strides in gene editing. Profluent, a California company, has released a research study where GenAI technologies can build new gene editors to edit human DNA, using the Nobel prize-winning technology called CRISPR.
- Implications for Personalized Medicine:These advancements provide doctors and scientists with new tools to create medicines and highly personalized treatments, potentially transforming healthcare.
AI’s Future Prospects in Biology and Genetics:
- DeepMind’s AlphaFold 3:The latest version of AlphaFold goes beyond proteins and delves into biochemical networks that make cells and organisms function. This could have far-reaching implications for our understanding of biology.
- Success Rates of AI-Discovered Drugs:A BCG study quoted by the Financial Times indicates that drugs discovered by AI have higher early-stage trials success rates, underscoring the potential of AI in drug discovery.
- Transcending Biology:While AI is often associated with creating stunning videos, travel itineraries, and food recipes, its real benefits to humankind could be deeper and more fundamental, particularly in helping humans transcend our biology.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Analyze the role of AI in personalized medicine and gene editing. What are the potential benefits and ethical considerations associated with these technologies?


Editorials
Context
India’s trade figures for 2023-24 reveal a trade deficit with nine of its top 10 trading partners, with the US being the only exception. These figures have sparked a need for a comprehensive analysis of structural, policy, and market factors to address the root causes of this trade imbalance.
Understanding India’s Trade Deficit:
- Introduction to the Issue:India has registered trade deficits with China, the UAE, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Iraq, Indonesia, Hong Kong, and South Korea, with a surplus only with the US, where exports exceeded imports by $36.7 billion in 2023-24. These top ten countries account for 52% of India’s total trade, making this data critical for analysis.
- Causes and Implications of Trade Deficit:A trade deficit can be an effect of various causes, such as increased import of raw materials or cheaper foreign products. While it can indicate increased purchasing power, it can also point to competitiveness issues at home.
- Persisting Trade Deficits:Trade deficits persist due to multiple reasons. Factors such as inverted duty structures and asymmetric tariff rates can hinder domestic manufacturing by incentivizing imports.
Boosting India’s Manufacturing Capabilities:
- Identifying Efficiently Produced Products:It’s crucial to assess our capacities to identify which products can be efficiently produced locally and traded globally. For instance, a substantial portion of India’s exports to the US in 2023-24 were in the category of electrical machinery and equipment.
- Emphasis on Manufacturing:In recent years, there has been an emphasis on boosting manufacturing with the vision of making India self-reliant. Initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive scheme, the introduction of GST, and measures related to the ease of doing business have given this sector the right impetus.
- Strategic Mapping of Manufacturing Capacities:Strategic mapping of India’s manufacturing capacities at a regional level will be a crucial exercise to attain greater self-reliance.
Diversifying India’s Export Basket:
- Need for Diversification:One key effort that lies ahead is diversifying our export basket and markets. Trade policy experts have acknowledged a welcome change in India’s export basket, which has seen a shift towards engineering and electronic goods.
- Shift to High-Value Goods:A shift to high-value goods reflects a move up the value chain and speaks of our competitiveness. India saw its electronic goods exports increase by around 54.8% in February 2024 compared to February 2023.
- Focus on Policies:Our focus should be on policies that make our manufacturing firms globally competitive. Thoroughly evaluating import-export figures, mapping our competitive advantage with each trade partner, and understanding how boosting manufacturing is a must to make India a global export hub.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Analyze the need for diversifying India’s export basket. How can a shift to high-value goods and a focus on policies that make our manufacturing firms globally competitive help India become a global export hub?


Editorials
Context
The tragic fire incident in a private neonatal care nursing home in New Delhi in May has highlighted the systemic failure of healthcare regulations in India. This incident has sparked a discussion on the need for a comprehensive approach to health regulations.
Issues with Health Regulations in India:
- Introduction to the Issue:The incident has brought to light the issues with health regulations in India. Despite having numerous health regulations, the private health sector is often seen as insufficiently regulated.
- Excessive and Unrealistic Regulations:Some states have over 50 approvals under multiple regulations that need to be complied with by every healthcare facility. Additionally, health-care quality standards set by the government are often unrealistic and difficult to implement.
- Inadequate Adoption of Regulations:The Clinical Establishments (Registration and Regulation) Act, 2010, enacted 14 years ago, has not been adopted by states due to its impractical provisions. Similarly, only 15% to 18% of government primary healthcare facilities meet the Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS).
Mixed Health-Care System in India:
- Public and Private Health Sectors:India has a mixed health-care system, with private healthcare facilities and providers delivering nearly 70% of outpatient and 50% of hospital-based services. People often choose private health facilities for their healthcare needs.
- Regulation Enforcement in the Private Sector:There is often an overzealous attempt to enforce regulations in the private sector. This can lead to a perception of unfairness and can discourage adherence to regulations.
- Delayed Approvals:The sluggish approval process for renewals is a major concern for facility owners. Applications submitted well in advance for renewal are often granted approval months later.
Need for Affordable Care:
- Variety in the Private Sector:The private sector is not a homogenous entity. It ranges from single doctor clinics and small nursing homes to large corporate hospitals. Single doctor clinics and small nursing homes often provide affordable care and are the first point of contact for many people.
- Role of Small Healthcare Facilities:Small healthcare facilities deliver a large share of health services at a fraction of the cost of big corporate hospitals. They are often the lifeline of health services, especially for middle-income and low-income populations.
- Addressing the Needs of the Population:The parents of the babies involved in the tragic incident opted for a private neonatal care nursing home, highlighting the need for affordable and accessible healthcare services.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Evaluate the role of the private sector in India’s mixed health-care system. How can regulation enforcement be improved in this sector?