

28th July 2025 (17 Topics)
Context
Eight pilgrims were killed and over 30 injured in a stampede at the Mansa Devi temple in Haridwar, Uttarakhand, on July 28, 2024.
Definition & Nature of a Stampede
- Stampede refers to a sudden, uncontrolled surge of a large crowd, often triggered by panic, fear, or excitement in congested spaces.
- A stampede becomes fatal when movement is restricted and pressure builds up, resulting in trampling or suffocation.
Key Causes of Stampedes
- Organizational Failures
- Inadequate Crowd Management: Absence of trained marshals or police supervision.
- Poor Planning: Lack of crowd modelling, emergency drills, or early warning systems.
- Communication Breakdown: No public announcement system or exit signage.
- Human Factors
- Panic/Fear: Often triggered by rumours, explosions, or fire
- Excitement/Euphoria: Seen during festivals, political rallies, or concerts.
- Aggression/Impatience: Linked to limited access, long queues, or poor crowd discipline.
- Infrastructure-Related Causes
- Overcrowding: Density exceeding 4-5 persons per square metre becomes dangerous.
- Poor Design: Narrow passageways, blocked exits, and lack of emergency escape routes.
- Adverse Conditions: Slippery terrain, low visibility, and staircases increase risk.
Impacts of Stampedes
- Human Costs
- Fatalities and Injuries: Severe fractures, internal injuries, and high death tolls.
- Psychological Trauma: Survivors often suffer from PTSD, panic attacks, or grief disorder.
- Economic and Infrastructure Loss
- Damage to public property, temporary structures, and religious or event infrastructure.
- Post-disaster expenditures on relief, rehabilitation, and structural upgrades.
- Administrative & Legal Fallout
- Investigations, judicial inquiries, and compensation claims.
- Demands for regulatory reforms, accountability, and standardised protocols for crowd events.
Stampede Incidents in India
- 2025 – Haridwar, Mansa Devi Temple: Panic triggered by a rumour about a snapped electric wire; led to chaos on a densely crowded stairway.
- 2025 – Bengaluru, Karnataka (RCB Final Celebration): Dozens injured during victory celebration of Royal Challengers Bengaluru at Brigade Road; crowd swelled beyond capacity, police overwhelmed.
- 2024 – Hathras, UP: Over 121 deaths due to lack of crowd control at a religious congregation.
- 2017 – Mumbai Station: 22 deaths during rush hour on an overcrowded footbridge.
- 2013 – Allahabad (Kumbh Mela): 36 deaths due to confusion over platform changes.
- 2008 – Naina Devi Temple, HP: 145 deaths after rumours of a landslide triggered panic.
- 2005 – Mandhardevi Temple, Maharashtra: Over 265 deaths during pilgrimage overcrowding.
NDMA Guidelines to Control Stampedes: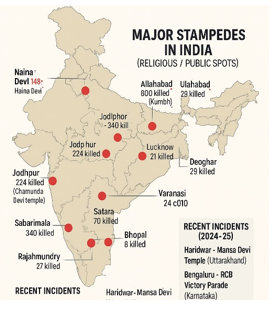
- Infrastructure Development: Ensure wide, safe pathways and adequate open spaces to accommodate large crowds, especially in high-risk areas.
- Route Segregation: Separate routes for normal, emergency, and express flows reduce congestion and aid vulnerable groups like children and elderly.
- Panic Management: Rapid response by trained staff is essential to defuse panic from triggers like rumors, loud sounds, or sudden movements.
- Community-Based Crowd Control: Emphasizes communication, cooperation, and volunteer involvement over force to manage public gatherings.
- Demand Management: Uses data on crowd trends, peak timings, and advance registration to regulate crowd inflow and avoid surges.
- Fire Safety: Enforces safe electrical setups and cautious use of LPG and fireworks to prevent secondary disasters during events.
Way Forward
- Use of Technology: Drone monitoring, AI-based crowd density estimation, mobile alerts.
- Urban Planning: Venue certification based on capacity, emergency pathways.
- Legal Measures: Enforcing Model Guidelines for Crowd Management (MHA, 2016) and NDMA guidelines.
- Training & Simulation: Mandatory mock drills before mass gatherings.
- Public Awareness: Clear signage, communication channels, and citizen participation.
More Articles


