

10th June 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
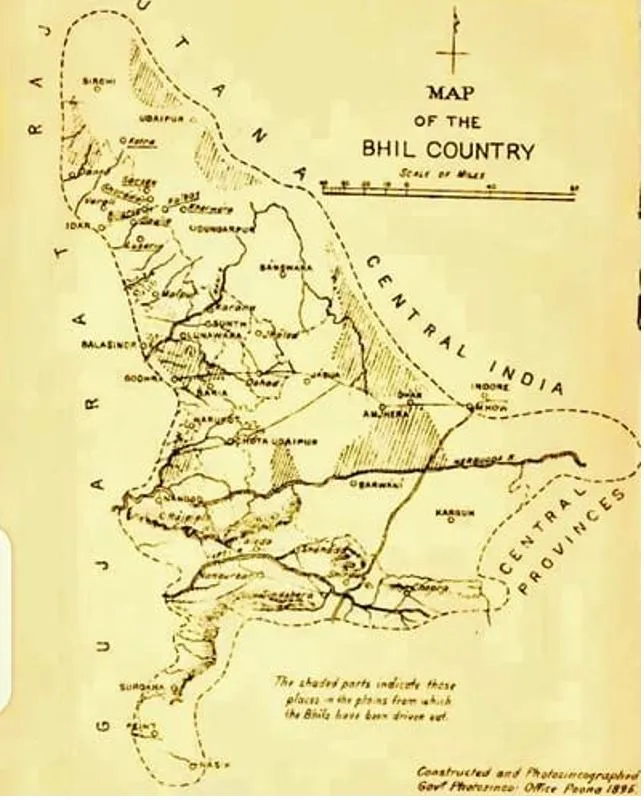
The demand for 'Bhil Pradesh', the idea of creating a new state for the Bhil tribal community from parts of Gujarat and three nearby states, has reared its head once again.
Who are the Bhils?
- The Bhils are one of India's oldest and second-largest tribal groups, known for their expertise in archery.
- The name "Bhil" likely originated from a Dravidian word meaning bow and arrow. The community is also known as the "Dhanush Purush of India" for having an excellent knowledge of Dhanush (
- They predominantly reside in states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra, with some migrating for job opportunities.
What is Bhil Pradesh?
- Bhil Pradesh is a proposed state aimed at addressing the socio-economic and cultural needs of the Bhil tribal community.
- It would include areas with significant Bhil populations across Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- The Bhils are demanding to carve out a separate state based on Article 244 (1) of the Constitution of India.
Why is it demanded?
- Historically, the Bhils have faced marginalization and socio-economic challenges. Despite their rich cultural heritage, they often feel neglected in the development plans of the states they inhabit.
- The demand for Bhil Pradesh stems from the desire to have more focused attention on their needs and development.
- This demand was first raised by Govind Guru, a Bhil social reformer and spiritual leader, after the tragic event of the Mangarh massacre in 1913.
- The government has implemented various measures like the Tribal Sub-Plan, Forest Rights Act, and reservation policies to address tribal issues, but the Bhils still feel the need for a separate state to ensure their voices are heard and their unique challenges are adequately addressed.
Government Initiatives:
- Along with reservation policies in education and employment, the Government of India has introduced several schemes and policies to uplift tribal communities, including the Bhils. These include the:
- Tribal Sub-Plan
- Forest Rights Act
- NREGA
- ICDS
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme
- Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act, 1996 (allows and ensures tribal self-rule for people living in scheduled areas).
- Constitutional Measures: Protection of tribal interests through the Fifth Schedule under Article 244(1) of the Constitution.



