

10th June 2024 (11 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
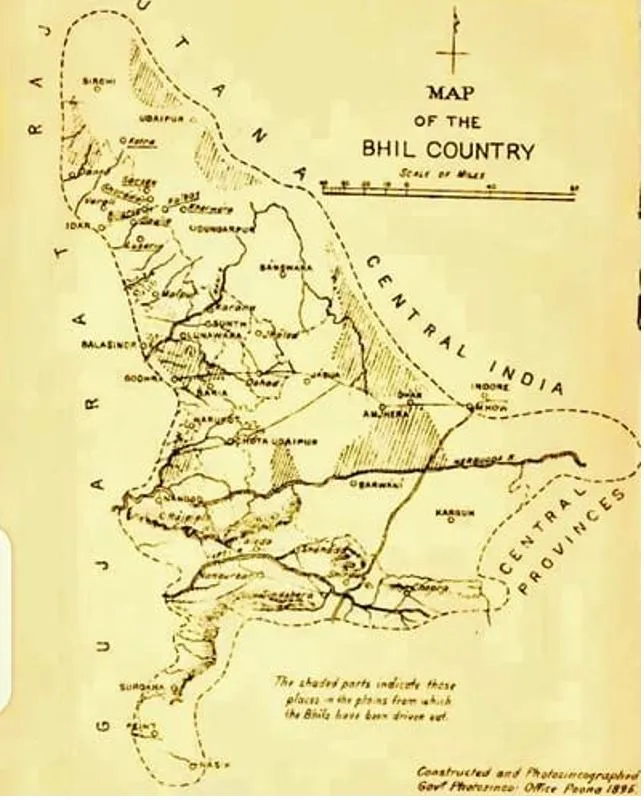
The demand for 'Bhil Pradesh', the idea of creating a new state for the Bhil tribal community from parts of Gujarat and three nearby states, has reared its head once again.
Who are the Bhils?
- The Bhils are one of India's oldest and second-largest tribal groups, known for their expertise in archery.
- The name "Bhil" likely originated from a Dravidian word meaning bow and arrow. The community is also known as the "Dhanush Purush of India" for having an excellent knowledge of Dhanush (
- They predominantly reside in states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra, with some migrating for job opportunities.
What is Bhil Pradesh?
- Bhil Pradesh is a proposed state aimed at addressing the socio-economic and cultural needs of the Bhil tribal community.
- It would include areas with significant Bhil populations across Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- The Bhils are demanding to carve out a separate state based on Article 244 (1) of the Constitution of India.
Why is it demanded?
- Historically, the Bhils have faced marginalization and socio-economic challenges. Despite their rich cultural heritage, they often feel neglected in the development plans of the states they inhabit.
- The demand for Bhil Pradesh stems from the desire to have more focused attention on their needs and development.
- This demand was first raised by Govind Guru, a Bhil social reformer and spiritual leader, after the tragic event of the Mangarh massacre in 1913.
- The government has implemented various measures like the Tribal Sub-Plan, Forest Rights Act, and reservation policies to address tribal issues, but the Bhils still feel the need for a separate state to ensure their voices are heard and their unique challenges are adequately addressed.
Government Initiatives:
- Along with reservation policies in education and employment, the Government of India has introduced several schemes and policies to uplift tribal communities, including the Bhils. These include the:
- Tribal Sub-Plan
- Forest Rights Act
- NREGA
- ICDS
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme
- Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act, 1996 (allows and ensures tribal self-rule for people living in scheduled areas).
- Constitutional Measures: Protection of tribal interests through the Fifth Schedule under Article 244(1) of the Constitution.


Mains Issues
Context
In the recent Lok Sabha Elections, the NDA emerged as the leading alliance, forming the government with a majority of seats. However, the Opposition bloc also had a significant presence in the Parliament. Despite their collective vote share, other regional parties and independents didn't win many seats.
What is FPTP?
- First Past the Post System (FPTP) is a voting system used in India for Lok Sabha and Legislative Assembly elections.
- It is also known as the simple majority system.
- In this system, the candidate with the most votes in a constituency wins, regardless of whether they have a majority.
- Advantages of FPTP:
- Simple and feasible, suitable for a large country like India.
- Provides stability to the government as the winning party/coalition can have a majority in the legislature without winning a majority of votes.
- Issues with FPTP:
- May lead to over or under-representation of political parties compared to their vote share.
- In some cases, a party with a minority of votes can still win a majority of seats.
Alternatives to FPTP:
- Proportional Representation (PR) system ensures representation of parties based on their vote share.
- Mixed Member Proportional Representation (MMPR) combines FPTP with proportional representation, providing stability and proportionate representation.
- In the commonly used 'party list PR' system, voters vote for a political party, not specific candidates. Parties are then allocated seats in legislative bodies based on their overall vote share. There's usually a minimum threshold (around 3-5% of the vote) for a party to qualify for seats.
- Implementation in India: If implemented in India, PR would ideally operate at each State/Union Territory level due to the federal nature of the country.
- International Practices: Some countries like Germany and New Zealand use MMPR, ensuring both stability and proportionate representation.


Mains Issues
Context
Starting August 1, 2024, insurance companies in India are mandated to settle health insurance claims through cashless methods. This move by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) aims to streamline and expedite the process of hospital bill settlement for policyholders.
Key-highlights of IRDAI’s decision:
- Cashless Settlement: Insurance companies must adopt cashless settlement of health insurance claims, ensuring smoother and faster processing of claims for policyholders.
- Procedures for Insurers: Insurers must establish dedicated Help Desks at hospitals to assist with cashless requests and provide pre-authorization through digital means.
- Timely Settlement: Insurers are encouraged to achieve 100% cashless claim settlement within a specified timeframe, minimizing the need for reimbursement except in exceptional circumstances.
- Claim Processing Timeframe: Insurers are required to decide on cashless authorization requests promptly, within one hour of receipt, and grant final authorization within three hours of discharge authorization from the hospital.
- Compensation for Delays: In case of delays beyond the stipulated timeframe, insurers are liable to cover any additional charges imposed by the hospital from their shareholder's fund.
- Dealing with Mortal Remains: In unfortunate instances of the policyholder's death during treatment, insurers must promptly process the claim and facilitate the release of the mortal remains from the hospital.
What are the likely impacts?
- Positive Impact: The move towards cashless settlement of health insurance claims is expected to alleviate the burden on policyholders, making the process more efficient and less stressful, especially during times of illness or emergencies.
- Reducing Challenges: With a significant percentage of policyholders facing difficulties in processing health insurance claims, the new mandate addresses concerns raised in surveys regarding claim rejection and time-consuming processes.
- Policyholder Rights: IRDAI emphasizes policyholders' rights, including the option to port policies between insurers and ensuring seamless transfer of underwriting details and claim history.
- Regulatory Oversight: The requirement for insurers to seek approval before repudiating claims and the establishment of clear procedures for claim processing aim to enhance transparency and accountability in the insurance sector.
- Improving Accessibility: By eliminating the need for policyholders to submit documents directly, the process becomes more accessible and convenient for individuals seeking health insurance benefits.
Fact Box:Indian Insurance market
Important Government Interventions
Other recent initiatives taken by IRDAI
|


Mains Issues
Context
India has taken a crucial step towards demand creation of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives in the country. Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) has issued Request for Selection (RfS) for Selection of Green Ammonia Producers for the production of Green Ammonia in India under Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Programme.
Implications for India's Energy Sector:
- Environmental benefits: The production of Green Ammonia holds immense promise for India's energy sector. By leveraging renewable energy sources for ammonia production, the country can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and mitigate environmental degradation.
- Energy security and development: Furthermore, the adoption of Green Hydrogen technologies not only enhances energy security but also fosters economic growth through job creation and technology development.
- Emergence as leader: By prioritizing the production of Green Ammonia and other clean energy derivatives, India is poised to emerge as a global leader in the clean energy transition.
- Self-reliance: With concerted efforts and strategic investments, the nation is well-positioned to achieve its goal of Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) while spearheading the global fight against climate change.
India’s position in Ammonia market
- India is positioning itself as a key player in the renewable ammonia
- India’s ambition to produce 5 million metric tons (mt) of renewable hydrogen by 2030 and secure a 10 per cent share of the global trade by that time underscores its commitment to renewable energy.
- Challenges: While India boasts nearly 100 renewable or low-carbon hydrogen projects with a combined capacity of 7.85 million mt, the challenge lies in finding a market for its renewable ammonia.
- Advantages for India: Despite these challenges, India's renewable hydrogen/ammonia is expected to remain competitive globally due to its cost advantages.
- National Green Hydrogen Mission 2023 waives interstate transmission charges for renewable energy and offers substantial subsidies, plays a pivotal role in driving down production costs.
- India's renewable energy sector benefits from various incentives, including cheap power, subsidies, low-cost loans, and readily available land, provided by federal and state governments.
- India enjoys a significant transport cost advantage over the Middle East in supplying to North Asia, further enhancing its competitiveness.
What is the ‘SIGHT Programme’?
- SIGHT Programme is a subcomponent of National Green Hydrogen Mission under Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE)
- This program aims to propel India towards self-reliance in clean energy through the production of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives.
- Implemented by: Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI)
- Under the SIGHT Programme, MNRE has already allocated 4.12 lakh Metric Tonnes (MT)/annum of Green Hydrogen production capacity and 1.5 GW/ annum of Electrolyzer manufacturing capacity.
|
Fact Box: Green Hydrogen
Green Ammonia
National Green Hydrogen Mission:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The new Cabinet is expected to approve a 100-day action plan focusing on animal health, dairy, and conservation. This plan aims to address challenges such as low availability of feed and fodder, poor livestock health, and the decline of indigenous breeds due to climate change.
Key Initiatives:
- Revamped Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM):
- The RGM will focus on developing and conserving indigenous bovine breeds to enhance milk production and make it more profitable for farmers.
- Private sector participation will be encouraged, with the formation of breeder associations in every state and Union Territory.
- Genetic upgradation techniques like in-vitro fertilization and genomic selection will be utilized to improve breed productivity.
- National Fodder Mission Convergence Framework:
- A convergence plan involving the agriculture and rural development ministries will be launched to increase fodder availability.
- Resources from both government and private sectors will be pooled to enhance fodder production, storage, and processing.
- The aim is to cultivate fodder on additional land and produce quality fodder seeds, with an allocated budget of Rs 300 crore.
- Animal Health System Support for One Health (AHSSOH):
- AHSSOH will focus on preventing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in animals, which occurs due to overuse of antibiotics.
- Research will be conducted to develop medicines that combat AMR effectively, without creating resistance.
Fact Box:About Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM)
India’s Dairy Sector (Key Statistics)
Government Initiatives:
|


Prelims Articles
Pakistan has confirmed the fifth polio case of the year, more than a fortnight after the victim's death, jolting the country's efforts to eradicate the crippling disease.
What is Polio?
- Polio, short for poliomyelitis, is a highly contagious viral disease that primarily affects children under 5 years old.
- It is caused by the
- Poliovirus spreads easily from person to person, mainly through contaminated feces entering the mouth (faecal-oral route). Less commonly, it can spread through contaminated water or food.
- Symptoms and Effects: Initially, poliovirus infects the throat and intestines, causing flu-like symptoms. In severe cases, it can invade the nervous system, leading to paralysis, especially in the limbs. In rare instances, it can be fatal.
- Variations of Poliovirus: There are three types of poliovirus:
- Wild Poliovirus Type 1
- Wild Poliovirus Type 2
- Wild Poliovirus Type 3
- Wild poliovirus types 2 and 3 have been eradicated globally, and type 1 remains in a few areas. Type 1 is most likely to cause paralysis.
- Vaccines available to fight polio: Inactivated poliovirus (IPV), Oral polio vaccine (OPV):
- According to the World Health Organisation, polio remains endemic in only two countries: Pakistan and Afghanistan.
India’s Case:
In 2012, the WHO removed India from the list of countries with active endemic wild poliovirus transmissioIndia launched the Pulse Polio immunisation programme in 1995 after a resolution for a global initiative of polio eradication was adopted by the World Health Assembly (WHA) in 1988.


Prelims Articles
Context
Sub Lieutenant Anamika B. Rajeev became the Indian Navy's first woman helicopter pilot during a passing out parade held in the naval air station INS Rajali at Arakkonam in Ranipet district.
Women in Defence Forces
Indian Army:
- Women officers now have opportunities for Permanent Commission in various branches, ensuring gender parity.
- Women candidates in National Defence Academy (NDA) has been opened, with cadets joining every six months.
- Women officers can now serve as pilots in the Corps of Army Aviation.
- Provision for enrolment of women as Other Ranks (ORs) in Corps of Military Police
Indian Navy:
- Women officers are recruited in all branches, except Submarine specialisation, since June 2023.
- Women officers serve on board warships and as Specialist Naval Air Operations (NAO)
- Women officers can join the Remotely Piloted Aircraft (RPA) stream.
- Entry for women cadets in NDA and Indian Naval Academy (INA) has been permitted, increasing vacancies for women cadets.
Indian Air Force:
- Facilities for women personnel are provided as per authorized scales.
- Recruitment of officers is gender-neutral, with women officers inducted in all branches and streams.
- Women officers can serve in combat roles without restrictions.
- Entry for women officers through NDA and NCC Special Entry has been initiated.
- Various induction publicity programmes are conducted to encourage women candidates to join IAF.
Fact Box: The numbers
|


Prelims Articles
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Coalition Government |
A coalition government is a government formed jointly by more than one political party |
|
2. |
First-past-the-post System |
It is a voting system, in which the candidate with the highest number of votes in a constituency is declared the winner. |
|
3. |
Hydrogen Line |
The "hydrogen line" refers to a specific frequency of electromagnetic radiation emitted by neutral hydrogen atoms. It has a wavelength of about 21 centimeters, which corresponds to a frequency of approximately 1420 megahertz (MHz). This spectral line is significant in astronomy because it is used to study the distribution and motion of hydrogen gas in the universe. |
|
4. |
Proportional Representation
|
It is a voting system requires the distribution of seats to be proportional to the distribution of the popular vote among competing political parties |


Editorials
Context
The maritime world was shaken by the crash of the container ship Dali into the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, United States, on March 26, 2024. The accident resulted in at least six fatalities and millions of dollars in property damage. The incident has drawn attention to India’s significant role in global shipping.
India’s Stake in Global Shipping
- India’s Role: India has become a key player in global shipping, with Indian seafarers manning many ocean-going ships. Remittances from these seafarers are equivalent to about 15% of all foreign direct investment that India receives annually.
- The Dali Incident: The crew of the Dali, which caused the Baltimore accident, is almost entirely Indian. The ship is managed by Synergy Maritime Group, a Singapore-based company run largely by Indians.
- Potential Financial Fallout: The Dali accident could result in the highest-ever marine insurance payout, surpassing the $1.5 billion paid out for the Costa Concordia cruise vessel capsizing in 2012. If it is proven that the managers neglected or avoided maintaining proper operating conditions, leading to the collision, there could be financial consequences for Synergy.
Implications for Indian Seafarers
- Reputation at Stake: The actions of Indian seafarers in global shipping reflect on India as a whole. The Dali accident could potentially damage the reputation of Indian seafarers.
- Questioning Competence: The final report on the Dali accident may question the competence and certification of Indian seafarers if it is found that botched or wrong operations by ship staff contributed to the accident.
- Government Intervention: The Indian government acted swiftly to prevent any hasty and ill-founded damage to the reputation of Indian seafarers. It successfully impleaded India as a Substantially Interested State as per the Casualty Investigation Code of the International Maritime Organization.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Discuss the economic impact of the global shipping industry on India's economy, focusing on the role of Indian seafarers and the challenges they face.


Editorials
Context
India and the U.S. have managed to settle seven long-standing trade disputes at the World Trade Organization (WTO), demonstrating the power of diplomacy in resolving trade frictions.
The Poultry Dispute
- Origins of the Dispute: Initiated by the U.S. in 2012, this dispute challenged India’s import restrictions on poultry products due to concerns about avian influenza. This dispute, which remained unresolved for over a decade, was the oldest of the seven disputes between the two countries.
- Resolution of the Dispute: After a decade of negotiations, India and the U.S. reached a mutually agreed solution, withdrawing their respective pending WTO cases. As part of the settlement, India dodged a yearly $450 million claim and agreed to reduce tariffs on select products such as cranberries, blueberries, frozen turkey, and premium frozen duck meat.
- Significance of the Resolution: While not the most economically significant dispute for India, its resolution represents a significant diplomatic breakthrough. It demonstrates that despite complicated domestic compulsions, major trading partners can effectively resolve sensitive trade matters through diplomatic channels.
Broader Implications for International Trade
- Amicable Resolutions: The successful settlement of multiple disputes showcases the potential for countries to achieve amicable resolutions, even in complex and contentious cases. It highlights the benefits of prioritizing negotiation over litigation.
- Multilateral vs. Bilateral Approaches: The paralysis of the WTO's Appellate Body since 2019 has necessitated out-of-the-box solutions for trade disputes. This settlement illustrates the viability of bilateral diplomatic efforts within the framework of multilateral litigation.
- Stable Trade Environment: The resolution of these disputes contributes to a more stable international trade environment, reducing the likelihood of prolonged conflicts and promoting smoother economic relations between major trading partners.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Discuss the significance of diplomatic negotiations in resolving international trade disputes, with reference to the recent settlement of trade disputes between India and the U.S. at the WTO.


Editorials
Context
The current global economic landscape, marked by frequent disruptions in supply chains and growing political polarization, underscores the need for a fundamental re-evaluation of economic theories and practices. Historical precedents suggest that paradigm shifts in economic thought are essential during times of significant technological and societal changes.
Challenges in Contemporary Economic Thought
- Inadequacy of Current Models: Despite an abundance of data, mainstream economic thinking and policymaking are failing to address the complexities of today's world. Critics argue that the focus on mathematical models has detracted from the field’s practical applicability to public policy.
- Need for Paradigm Shifts: Major turning points in history, such as the Industrial Revolution, necessitated new economic theories to understand and manage the resulting societal changes. Similarly, the digital revolution and artificial intelligence today demand a rethinking of economic fundamentals.
- Interconnected Issues: The separation of economics from political science has created an artificial divide that hinders a comprehensive understanding of modern global issues. The rise of game theory offers a framework to bridge this gap, integrating political and economic analysis.
Historical Context and Lessons
- Industrial Revolution Insights: The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in production and labor, prompting pioneering works like Adam Smith's "The Wealth of Nations" and Léon Walras’s "Elements of Pure Economics." These works laid the groundwork for necessary policy interventions and economic reforms.
- Shift to Neoclassical Economics: Following Walras, economics became more focused on mathematical modeling, which initially served public policy well. However, the assumption of perfect information embedded in neoclassical economics proved to be unrealistic.
- Information Asymmetry Breakthroughs: Economists like George Akerlof, Joseph Stiglitz, and Michael Spence highlighted the impact of asymmetric information, challenging core neoclassical assumptions and leading to policy changes that better protected consumers and workers.
Implications of the Digital Revolution
- Redefining Labor and Trade: The digital revolution and AI are transforming labor markets and international trade, creating new forms of economic interactions and conflicts. Policymakers need to recognize these changes and adapt accordingly.
- Firefighting vs. Structural Change: Current economic policies often react to crises rather than addressing underlying systemic issues. Just as developing non-flammable materials is better than firefighting, economic policies should aim for long-term resilience.
- Reviving Political Economy: Returning to the classical tradition of political economy can provide the necessary tools to understand and navigate the complex interplay between economics and politics in the modern world.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Analyze the implications of the digital revolution on labor markets and international trade. What changes in economic policy are needed to address these challenges effectively?





