

12th May 2025 (12 Topics)
Context
Pakistan fired its ballistic missile Fatah-II, an improved version of the Fatah-I system with better range and accuracy, but was successfully intercepted by the Indian defence system in Haryana's Sirsa.
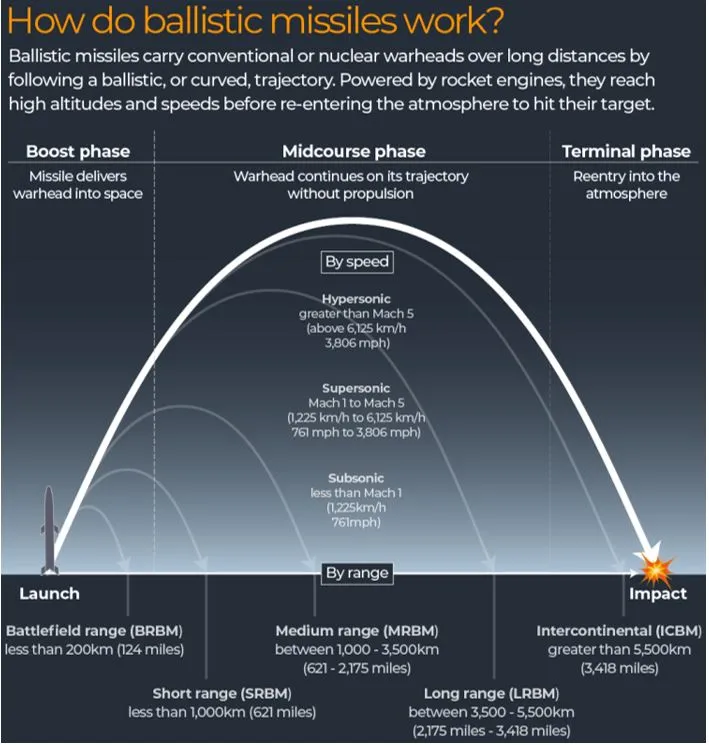
What is a ballistic missile?
- A ballistic missile is a missile which uses projectile motion (something which moves in the air when launched, under the influence of gravity, with air resistance neglected) to hit the target.
- Most of the flight of these missiles are unpowered, as the weapons are powered only for short periods.
- There are two types of ballistic missiles –
- Short-range (SRBM), typically used during wars and satellites within the Earth's atmosphere
- larger ones have the capability to travel outside it
- ICBM (intercontinental ballistic missile) are the ballistic missiles with the greatest range, capable of full orbital flight.
- Types of ballistic missiles
- Tactical ballistic missile (TBM): Range less than 300 km
- Short-range ballistic missile (SRBM): Range from 300 to 1,000 kilometres (190 to 620 mi)
- Medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM): Range from 1,000 to 3,500 kilometres (620 to 2,170 mi)
- Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM): Range from 3,500 to 5,500 kilometres (2,200 to 3,400 mi)
- Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): Range greater than 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi)
Fact Box: Fatah-II
|
More Articles


