14th April 2025 (12 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
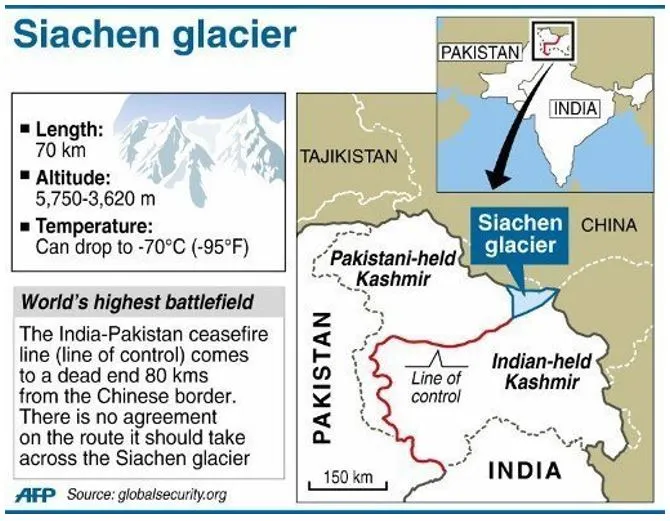
April 13, 2025, marks 41 years since India launched Operation Meghdoot (1984) and captured the Siachen Glacier.
Strategic Significance of Siachen
- Siachen Glacier is a 76-km long glacier in the Karakoram Range of Ladakh.
- Located at a height of around 20,000 feet in the Karakoram Mountain range, the Siachen Glacier is known as the highest militarised zone around the world.
- It lies between:
- Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) in the west
- Shaksgam Valley (illegally given to China by Pakistan in 1963) in the north
- Depsang Plains and LAC with China in the east
- Strategic wedge: Siachen sits like a “strategic wedge” between Pakistan and China — giving India control over a crucial triangular zone in the high Himalayas.
- The region controls key high-altitude terrain. It overlooks:
- Gilgit-Baltistan (PoK) on the west
- Depsang Plains and Karakoram Pass on the east
- Shaksgam Valley (ceded to China) on the north
- Indian Army dominates Saltoro Ridge, giving a military advantage over both Pakistan and China.
What’s the Dispute?
- After the 1947-48 war, the Karachi Agreement (1949) defined a Ceasefire Line (CFL).
- After the 1971 war, the Shimla Agreement (1972) renamed it Line of Control (LoC).
- BUT — from Point NJ 9842 (a map reference), the LoC is not clearly defined.
- The CFL said it extends “northwards to the glaciers” — but India and Pakistan interpret this differently:
- Pakistan: Wants the line to move northeast to Karakoram Pass (which would give it control of Siachen).
- India: Interprets “northwards” as running along the Saltoro Ridge, which it captured in 1984.
How Did India Capture Siachen? (Operation Meghdoot)
- On April 13, 1984 (Baisakhi Day), under PM Indira Gandhi, India launched Operation Meghdoot.
- Indian troops from 4 Kumaon Regiment were airlifted to Bilafond La (a 17,880 ft mountain pass).
- The Indian Army occupied key passes along the Saltoro Ridge and raised the national flag.
- Pakistan tried to recapture these areas but failed.
- Today, nearly all the aircraft of the Air Force, including Rafale, Su-30MKI, Chinook, Apache, Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Mk III and Mk IV, Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) Prachand, MiG-29, Mirage-2000, C-17, C-130 J, IL-76 and An-32 operate in support of Operation Meghdoot.
Why is China Now a Bigger Concern?
- China, not Pakistan, is now seen as the bigger threat around Siachen.
- Chinese PLA could launch a westward military thrust through the Depsang Plains to:
- Cut off the DSDBO Road (India’s lifeline to Karakoram Pass)
- Capture Saser La, which could threaten the Siachen base camp
- China’s Silent Expansion Near PoK: China is present in PoK under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). Karakoram Highway (part of CPEC) passes close to Siachen. China also sends workers as “dam and road builders” — increasing influence near Indian positions.
- India has deployed tanks, artillery, advanced systems and troops to stop such a move.
- Strategic Infrastructure Nearby: DSDBO Road (255 km) links Leh to Daulat Beg Oldie, near Karakoram Pass. If China cuts this road, Indian access to northern Ladakh is threatened.


Mains Issues
Context
Violent protests broke out in Murshidabad district, West Bengal over the Waqf (Amendment) Act, leading to communal tensions, deaths, and property destruction. Allegations of police inaction, mob violence, and selective targeting of community properties raised serious governance and federal concerns.
Federalism: Breakdown in Law and Order
- Law and order is a State subject (List II, Seventh Schedule) under the Indian Constitution.
- However, when state machinery fails or is unable to control violence, the High Court or Centre can step in to ensure rule of law.
- In West Bengal, State police allegedly failed to respond promptly to distress calls. High Court observed that it "cannot turn a blind eye" and ordered Central Force deployment under Article 226.
Relevant Constitutional Provisions:
|
- However, it raises questions about:
- State responsibility in maintaining order
- Role of the judiciary in federal checks
- Need for coordination between State and Centre during internal disturbances
Pattern of Communal Mobilisation over Property Issues
- Disputes over religious or community property often escalate into violence, especially when:
- There is unclear legal jurisdiction
- Communities feel excluded from policy dialogue
- In this case, alleged targeted attacks on certain community homes and businesses show:
- Risk of communal polarization
- Failure to uphold the secular mandate of the State


Mains Issues
Context
In a key ruling, the Supreme Court set clear limits on governors' powers, holding they cannot indefinitely delay action on state bills. The court addressed growing concerns over governors misusing discretionary powers to obstruct elected state governments.
Supreme Court’s Judgement (2024)
- Governor must return bills “as soon as possible” with reasons if withholding assent.
- If a bill is repassed by the Assembly, the Governor is constitutionally bound to give assent — cannot reserve it for the President.
- Indefinite delays or inaction are unconstitutional.
- Governor’s legislative conduct is subject to judicial review.
- Used Article 142 to grant “deemed assent” to 10 bills, bypassing the Governor entirely.
- End of the Governor’s ‘Pocket Veto’: The court outlawed indefinite delays, effectively ending the misuse of pocket veto by governors. It asserted that “withholding without time limit or reason” violates the Constitution. It introduced timeframes for actions:
- 1 month to assent or act on ministerial advice.
- 3 months to return/reserve bills if not following advice.
- 1 month to assent after repassage.
Why this ruling matters?
- The ruling reinforces federalism and democratic accountability. It protects elected state legislatures from unelected constitutional heads.
- It provides legal clarity amid rising Centre–State tensions (similar issues in Kerala, Punjab, Telangana, West Bengal).
- Furthermore, it strengthens the role of judicial review in executive delay tactics.
Key Provisions
|


Prelims Articles
Context
In a significant move, the centuries-old Pilicode Rayaramangalam temple in Kasaragod district, Kerala, has opened its inner quarter (nalambalam) to devotees from all communities, marking the end of caste-based entry restrictions.
About the Temple
- Sree Rayaramangalam Bhagavathy temple is located at Thottam-Padne Road at Pilicode in Kasaragod district, Kerala.
- The temple is dedicated to Goddess Bhadrakali.
- Its rituals are managed by priests from the Kalagattathil illam, an ancestral Brahmin family.
- The temple has long adhered to strict customs.
- Only the tantri has access through the narrow passageway between the inner quadrangle and the sanctum sanctorum. Complex rituals are performed in that space.
- Traditionally, only Brahmins and Ambalavasis had unrestricted access to the nalambalam, while individuals belonging to certain other castes, including Nairs and the Maniyani community, were permitted entry only on specific ceremonial occasions such as poorolsavam and patolasavam.


Prelims Articles
Context
India, in partnership with nine African countries, launched a major naval exercise called AIKEYME 2025 off the coast of Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania. This exercise, held over six days, is a significant step in enhancing maritime security collaboration between India and the African continent.
What is AIKEYME?
- AIKEYME stands for Africa-India Key Maritime Engagement.
- It is a multilateral naval exercise co-hosted by the Indian Navy and Tanzania People's Defence Force.
- AIKEYME is part of India’s evolving strategy to become a net security provider in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), while also fostering South-South cooperation in alignment with its Act East and Africa policy.
- It’s the first edition of this initiative, aiming to strengthen maritime cooperation between India and key African maritime nations.
- In addition to India and Tanzania, the participating African countries are: Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles and South Africa.
- The exercise supports India’s MAHASAGAR Vision — “Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions”.
- This vision focuses on:
- Strengthening ties with the Global South
- Promoting collective security
- Enhancing regional development
India’s defence engagement with Africa
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Kerala became the first state in India to achieve total digital literacy. This milestone was achieved through the ‘Digi Kerala’ initiative, implemented by the Local Self-Government (LSG) department.
What is Digital Literacy?
- Digital Literacy refers to the “The ability of individuals and communities to understand and use digital technologies for meaningful actions within life situations.”
- It goes beyond just being able to use a computer or smartphone; it involves the ability to use the internet for various purposes such as communication, accessing government services, online banking, and using social media responsibly.
Government’s Key Initiatives to Improve Digital Literacy:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan’s Dharmadam constituency in Kannur has been declared the state’s first ‘extreme poverty-free’ constituency (April 2025). This milestone is part of Kerala’s broader plan to eradicate extreme poverty across the state by 1 November 2025, making it a model for inclusive development.
What is Extreme Poverty?
- Extreme poverty refers to a condition where a household lacks access to the basic minimum requirements of human survival, including:
- Food availability
- Healthcare
- Basic income
- Adequate housing
- These four indicators were used by the Kerala government to identify and classify extremely poor families through a grassroots-level survey.
- Extreme poverty is defined by the UN as living on less than USD 1.90 a day.
- India’s poverty line
- In India, the official consumption-based poverty line is still the Tendulkar Line, which is close to the World Bank's USD 1.9 a day line.
- The Tendulkar Expert Group chaired by economist Suresh Tendulkar in 2009 was formed to review the methodology for poverty estimation.
- The committee finalised the per person per day consumption figure of Rs 32 a day for urban areas and Rs 26 a day for rural areas.
- The national poverty line for 2011-’12 was estimated at Rs 816 per capita per month for rural areas and Rs 1,000 per capita per month for urban areas.
Rangarajan Committee
Major Government Initiatives to Eradicate Poverty in India:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
India has successfully tested its indigenously developed Laser-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system, placing it among a select group of countries (US, China, Russia) possessing high-power laser-based military technology.
What is the Laser-DEW System (Sahastra Shakti)?
- Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs) use high-energy laser beamsto damage or destroy enemy targets.
- Unlike traditional kinetic weapons, laser systems offer instantaneous engagement, precision targeting, and low per-shot cost, making them ideal for neutralizing low-RCS (Radar Cross Section) threats like drones and incoming munitions.
- It is developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Apart from India, only the US, China and Russia can disable weapons using the technology.
- How does it work?
- The Mk-II(A) Laser- Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) is one of the most potent counter drone systems in the world due to its lightning speed of engagement, precision and lethal action within a few seconds.
- The laser system engages fixed-wing drones from a long range and can thwart multiple drone attacks at a time, destroying surveillance sensors and antennae.
- Once a target is identified by the Laser-DEW system's radar or its inbuilt Electro Optic (EO) system, it uses an intense beam of powerful light (Laser Beam) to cut through the target, causing structural failures or even more lethal damage.
- The development of this laser weapon can lower the risk of collateral damage and reduce reliance on expensive ammunition during conflict.


Prelims Articles
Context
India has developed its first automated bat monitoring and detection system – BatEchoMon, marking a major technological and ecological milestone in wildlife research.
What is BatEchoMon?
- BatEchoMon (Bat Echolocation Monitoring) is India’s first automated bat monitoring system.
- It detects and analyses bat echolocation calls in real-time using a combination of:
- Ultrasonic detector (Audiomoth)
- Raspberry Pi microprocessor
- AI-based algorithm (convolutional neural network)
- It identifies bat species, records activity patterns, and generates audio and visual data (spectrograms).
- It runs autonomously—activating at sunset—and is powered by solar energy with Wi-Fi-enabled data transmission.
- Developed by researchers at the Indian Institute for Human Settlements (IIHS), it is a low-cost, modular, and efficient solution for large-scale bat ecology research in India.


Editorials
Context
B.R. Ambedkar’s legacy has witnessed a historic reversal of public perception — from being vilified by dominant caste ideologues and sidelined by political elites, to becoming a central icon in Indian political and social discourse. His name now holds such significance that even its mere invocation in Parliament can trigger political storms, reflecting the growing assertion of Dalit identity and mainstream political appropriation of Ambedkar’s symbolism.
AMBEDKAR’S TRANSFORMATION FROM MARGINS TO MAINSTREAM
- Reversal of Historical Marginalisation: Ambedkar, once dismissed as sectarian by Congress and the Left, has emerged as one of the most invoked personalities in modern India — a result of the politicisation and consolidation of Dalit identity that dominant caste-led parties now tactically acknowledge.
- Contestation of Dalit Iconisation: Despite frequent desecration of his statues and social hostility, Dalits’ reverence for Ambedkar has persisted, prompting resentment and moral scrutiny from sections of the elite who fail to grasp the depth of his symbolic and lived legacy.
- Reductionist Public Discourse: The prevailing narratives either reduce Ambedkar to a mere tool of electoral politics or question the emotional devotion of Dalits, both of which obscure the philosophical depth, ethical rigor, and political foresight of his work.
PHILOSOPHICAL VISION AND POLITICAL STRATEGY
- Emphasis on Institutional Safeguards: Unlike Gandhi or Nehru, who relied on moral appeals or modernisation, Ambedkar advocated constitutional protections, enforceable rights, and institutional reforms to safeguard minorities against religious majoritarianism and caste dominance.
- Rewriting Indian Historiography: Ambedkar challenged the glorified narratives of ancient Hindu civilisation and anti-colonial nationalism, and instead centred Dalit-Bahujan experiences, providing a counter-history to mainstream historiographical traditions.
- Intellectual Integrity amid Hostility: He critiqued not just Hindu orthodoxy and British colonialism, but also nationalist icons who failed the oppressed — while simultaneously recognising the colonial contribution of introducing equality before law, a key foundation for justice in hierarchical India.
CONTEMPORARY RELEVANCE & MISSING STRATEGIC DEPTH
- Emblem of Resistance and Assertion: Today, Ambedkar is a unifying symbol for various marginalised groups — from sanitation workers to students and rural Dalit women, he embodies dignity, rights, and resistance in the face of systemic oppression.
- Strategic Vacuum in Modern Ambedkarite Movements: Contemporary Ambedkarite activism often lacks the rigour, spontaneity, and tactical foresight that Ambedkar displayed during events like the Round Table Conferences and Simon Commission, where he persistently demanded separate electorates and proportional representation.
- Relevance in Present Socio-Political Landscape: In a time when Dalit-Bahujan material needs are eclipsed by cultural conflicts, Ambedkar’s anti-hegemonic, emancipatory framework remains a radical blueprint for justice and equity, especially in today’s polarised democracy.
Practice Question
Q. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s vision extended beyond legal drafting to a radical reimagining of Indian democracy and social justice. Analyse the relevance of Ambedkar’s constitutional and political philosophy in the context of contemporary socio-political challenges in India.


Editorials
Context
India is at a pivotal moment to position itself as a global talent hub, with high-income countries projected to face a labour shortfall of 40–50 million by 2030, increasing to 120–160 million by 2040. Despite its large and young workforce, only 1.3% of India’s population are international migrants, far behind countries like Mexico (8.6%), Philippines (5.1%), and Bangladesh (4.3%), indicating huge untapped potential for increasing remittance income and legal circular migration.
DEMOGRAPHIC ADVANTAGE & REMITTANCE POTENTIAL
- India’s Untapped Migration Reserve: India’s international migrants make up only 1.3% of its population, yet they contribute $125 billion (3% of GDP) in annual remittances, exceeding any single sector of merchandise exports.
- Global Labour Shortage: An Opportunity: High-income nations are projected to face a labour gap of up to 160 million by 2040, especially in healthcare, engineering, teaching, and construction, creating a pressing demand for both skilled and semi-skilled workers.
- Developmental Impact of Remittances: A global study across 71 low-income countries shows a 10% rise in remittances reduces poverty by 3.5%, making migration a more impactful poverty-alleviation tool than merchandise exports.
STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR MIGRATION ECOSYSTEM
- Institutional Framework for Migration Governance: A centralised migration department under the MEA, supported by state-level units and embassy-based migration desks, is vital to coordinate recruitment, protect worker rights, and reintegrate returnees — drawing from the Philippines’ model.
- International Skills Recognition and Mobility: Aligning India's skilling ecosystem with international certification standards, promoting foreign language training, and pursuing Mutual Recognition Agreements (MRAs) can facilitate smoother overseas employment.
- Financial Access for Migrants: Migrant training and placement costs range from Rs 1–2 lakh (GCC) to Rs 5–10 lakh (Europe). India should explore financing mechanisms like the Philippines’ ESA-pay model, where employers cover pre-departure costs.
POLICY INITIATIVES FOR SUSTAINABLE CIRCULAR MIGRATION
- Bilateral Migration Agreements: India must negotiate government-to-government (G2G) mobility pacts to streamline visa norms, enable qualification recognition, and enhance cultural integration, following the Philippines’ agreements with 65+ countries.
- Regulation through a Dedicated Mobility Industry Body: Establishing a national mobility industry association can help formalise the recruitment sector, ensure ethical hiring standards, and bridge industry-government coordination gaps.
- Migrant Welfare and Reintegration Measures: Adopting ILO-compliant welfare norms—such as minimum wage, safe housing, legal aid, and post-return support—will ensure migrants’ protection and help them contribute to local development on return.
Practice Question
Q. India’s demographic dividend, if harnessed through a well-planned circular migration policy, can become a key driver of economic growth and global influence. Critically examine this statement in light of the current global labour shortage and India’s migration ecosystem.


Editorials
Context
The Supreme Court, in State of Tamil Nadu vs Governor of Tamil Nadu & Anr., ruled that the Governor's inaction on State Bills was unconstitutional, asserting that the Governor must act on the advice of the Council of Ministers and cannot withhold assent indefinitely or refer Bills to the President without valid grounds.
CONSTITUTIONAL POSITION OF THE GOVERNOR
- Bound by Aid and Advice: Under Article 163 and 200, the Governor is a nominal head and is constitutionally bound to act on the aid and advice of the elected State government, barring specific exceptions.
- No Absolute Veto: The Court rejected the Union's argument that Article 200 allows the Governor to withhold assent indefinitely, stating that such power would violate the principle of legislative supremacy.
- Governor is Not an Independent Authority: The Governor is not an autonomous constitutional actor but a constitutional functionary constrained by democratic norms and legal mandates.
ARTICLE 200 INTERPRETATION & COURT’S FINDINGS
- Limited Options Under Article 200: The Governor may only (1) grant assent, (2) withhold and return for reconsideration, or (3) reserve the Bill for President — with no fourth option of absolute rejection.
- No Personal Discretion in General Bills: Discretionary power is limited to cases affecting High Court powers, matters under Article 31C, or Bills threatening constitutional values — not ordinary State legislation.
- Judicial Review of Governor’s Conduct: Although Article 361 protects Governors from personal liability, their official actions are open to judicial scrutiny if they undermine constitutional governance.
SUPREME COURT’S REMEDY & FEDERAL IMPLICATIONS
- Doctrine of Deemed Assent: Using Article 142, the Court ruled that the 10 Bills re-passed by Tamil Nadu Assembly are deemed to have received assent on the date they were re-submitted to the Governor.
- Checks Against Federal Overreach: The ruling reinforces India’s federal architecture by curbing arbitrary interventions by centrally-appointed Governors in State legislation.
- Upholding Representative Democracy: The judgment reiterates that the Governor must uphold the will of the elected legislature and not act as a political disruptor.
Practice Question
Q. “The role of the Governor is not to obstruct but to uphold the constitutional functioning of the State.” In light of recent judicial pronouncements, critically examine the discretionary powers of the Governor under Article 200 and their implications for federalism in India.