

2nd August 2024 (11 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
The Supreme Court of India has made a landmark decision allowing the sub-categorization of Scheduled Castes (SCs) in reservations. This decision came from a 6:1 verdict by a seven-judge Constitution bench. The ruling permits states to provide more nuanced protection to underrepresented groups within the broader SC category, acknowledging that SCs are not a homogeneous group.
Key Highlights
The Supreme Court allowed the sub-categorization of Scheduled Castes for reservation purposes. It allowed the sub-categorization, providing a legal basis for states to address disparities within the SC community.
Sub-classification does not violate the principle of equality enshrined under Article 14 of the Constitution.
Creamy Layer: The court emphasised the necessity to exclude the 'creamy layer' within the Scheduled Castes from reservation benefits intended for SC categories.
- Currently, this concept is only applied to reservations for Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
The current ruling overturns the 2004 decision (EV Chinnaiah vs State of Andhra Pradesh), allowing states to provide differentiated reservations within the SC category.
- The 2004 judgment in EV Chinnaiah vs State of Andhra Pradesh held that SCs were a homogeneous group, and any sub-classification was impermissible.
Implications: The ruling is significant for states wanting to give greater protection to underrepresented castes within the SC category, addressing disparities among different SC communities.
Need for Sub-Categorization
- Addressing Inequality: The sub-categorization aims to address inequalities within the SC category, where some castes benefit more from reservations than others.
- Better Representation: It ensures that the most disadvantaged groups within the SC category receive adequate representation and benefits.
- Historical and Empirical Evidence: The decision is based on evidence that shows SCs are not a homogeneous group, and some sub-castes are more underrepresented and disadvantaged.
Impact
- State Policies: States can now create policies that provide targeted benefits to the most disadvantaged SC sub-castes.
- Reservations: The ruling impacts reservation policies in education and public employment, ensuring a more equitable distribution of opportunities.
- Wider Protection: Underrepresented castes within the SC category will receive wider protection and support, addressing historical inequalities.
- Future Legislation: The ruling sets a precedent for future legislation and policies related to reservations and affirmative action in India.
Fact Box: The concept of ‘Creamy Layer’In India, the 'creamy layer' refers to the relatively affluent and better-educated members of the OBCs who are excluded from reservation benefits in government jobs and educational institutions. This ensures that reservations benefit the genuinely underprivileged sections of OBCs. The concept was introduced following the Supreme Court's judgement in the Indra Sawhney case (1992), also known as the Mandal Commission case. Criteria for determining the creamy layer
|


Mains Issues
Context
The Indian government is set to introduce the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024, in the Lok Sabha.
Key-highlights of the Bill
- The bill aims to create a comprehensive disaster database at national and state levels and establish an Urban Disaster Management Authority for state capitals and major cities with Municipal Corporations.
- Disaster Database: This database will include disaster assessments, fund allocation details, expenditure reports, preparedness and mitigation plans, and a risk register categorized by type and severity of risk.
- Empowerment of NDMA and SDMA: The bill seeks to empower the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and the State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) to independently prepare disaster plans, replacing the reliance on plans made by the National and State Executive Committees.
- The NDMA will also be authorized to appoint experts and consultants as necessary.
- The NDMA will regularly assess a wide spectrum of disaster risks, including those from extreme climate events and other potential threats, even if such disasters have not yet occurred.
- Statutory Recognition: The bill will grant statutory recognition to existing bodies like the National Crisis Management Committee and the High-Level Committee.
- The amendment aims to integrate disaster management more effectively into development plans, aligning with the recommendations of the 15th Finance Commission.
- State Disaster Response Force: The bill proposes that state governments establish a State Disaster Response Force.
- New Section 60A: This section will empower both the Central and State Governments to direct individuals to take necessary actions or refrain from them to mitigate disaster impacts, with penalties for non-compliance not exceeding ?10,000.
Need for Disaster Management in India
- India is among the world's most disaster-prone countries with 27 of its 29 states and seven union territories exposed to recurrent natural hazards such as cyclones, earthquakes, landslides, floods and droughts.
- Disasters were historically perceived as inevitable or divine interventions. However, now two primary phenomena have intensified disaster risks:
- Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns, excessive rainfall leading to floods, extreme temperatures, formation of glacial lakes threatening ecosystems, and impacts on food security, water scarcity, and infrastructure.
- Unplanned Development: Rapid and unguided development in transportation, energy, urbanization, and tourism, which, although meant to improve quality of life, increase disaster vulnerability.
- Climate change and unplanned development necessitate a systematic approach to manage disasters.
- Effective disaster management (DM) includes a defined cycle encompassing prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery.
Current Structure of Disaster Management in India
- National Level:
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA): Policy-making body.
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF): Specialized force for disaster response.
- National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM): Focuses on training, research, and knowledge dissemination.
- State Level:
- State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs): State-level policy and planning.
- State Disaster Response Forces (SDRFs): State-level response units.
The Disaster Management Cycle
- Prevention and Mitigation: Initial measures to prevent disasters and reduce their impact.
- Preparedness: Capacity building through training and resource allocation.
- Response: Immediate relief and rescue operations with trained personnel and modern technology, focusing on saving lives and livelihoods.
- Recovery: Assessing damage, securing resources, and rebuilding to create a more resilient environment.
Recent Developments
- Early Warning Systems: Adoption of the Common Alerting Protocol (CAP) for disseminating warnings and advisories to the public via mobile networks.
- International Cooperation: Active participation of the NDRF and Indian Armed Forces in international disaster relief missions, e.g., Nepal earthquake (2015), Japan’s triple disaster (2011), Turkey earthquake (2023).
- G20 Leadership: India prioritized DRR during its G20 presidency in 2023, emphasizing early warning technologies and disaster risk financing.


Mains Issues
Context
The Budget 2024-25 promised a policy for promoting pumped storage projects to enhance electricity storage and integrate renewable energy effectively.
Why Pumped Storage?
- Ambitious Renewable Targets: India aims to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil power by 2030. In two years (2021-2023), it added 23 GW of non-fossil capacity, with 7.5 GW from wind and solar in just eight months of 2023-24.
- Variable Nature of Renewables: Renewable power generation, now over 10% of total generation, varies significantly, necessitating efficient storage solutions.
- State-of-the-Art Forecasting: Advanced forecasting techniques help predict renewable power variations, allowing grid operators to plan power generation from other sources accordingly.
- Types of Pumped Storage:
- On-River Projects: Similar to conventional hydroelectric projects, using river-supplied reservoirs.
- Off-River Projects: Use two reservoirs at different elevations in a closed loop, pumping water to the upper reservoir when surplus power is available and releasing it to generate power when needed.
Benefits of Hydro Power:
- Quick Response: Hydro power generation can ramp up or down in seconds, unlike coal and nuclear plants that need hours of notice.
- Support During Crises: Hydro power helped prevent blackouts during the pandemic's lights-off campaign.
Energy Storage Solutions:
- Pumped Storage: A preferred method for large-scale energy storage, using water to store and release energy, similar to a large battery.
- India’s Existing Capacity: India currently has 3.3 GW of pumped storage with plans to expand significantly to meet renewable targets.
- Global Leaders: China leads with 44 GW of pumped storage supporting 1,300 GW of wind and solar.
Case Study: Kadamparai Pumped Storage Plant
Integration with Renewable Energy:
|


Prelims Articles
Cloudbursts hit various locations in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand, leading to casualties.
What is Cloudburst?
- A cloudburst is a sudden, intense localised rainfall where more than 100 millimetres of rain falls in an hour, often causing flash floods.
- The phenomenon responsible is called ‘orographic lift’. Warm air currents push rain-ready clouds upwards. As they rise, water droplets grow larger and new ones form.
- These dense clouds eventually burst, releasing torrential rain over a small area. This can quickly cause water bodies to overflow.
- Cloudbursts are more common in mountainous regions because the terrain causes moisture-laden air to rise quickly along mountain slopes.
- Prediction: A doppler-radar system is ideal for predicting cloudbursts. After the 2013 calamity, there were calls to equip monitoring stations in cloudburst-prone areas with this technology.


Prelims Articles
Context
India has been elected as the Vice Chair of the Supply Chain Council under the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF).
About Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF):
- Launch: May 2022 in Tokyo, Japan.
- Members: 14 countries from the Indo-Pacific region, including the USA, India, Japan, Korea, and others.
- Objective: To enhance economic cooperation, growth, stability, and prosperity among partner countries in the region.
- Key Pillars of IPEF: Trade, Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, Fair Economy, Supply Chain Resilience
- Significance:
- IPEF focuses on strengthening and diversifying supply chains to make them more resilient against disruptions.
- It enhances the competitiveness of critical supply chains in the region.
- India's Role: India's election as Vice Chair of the Supply Chain Council signifies its critical role and commitment to enhancing supply chain resilience and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region. This involvement aligns with India's broader economic strategy and its efforts to integrate more deeply into global supply chains.


Prelims Articles
Context
Privilege Motion has been moved against PM Modi in Lok Sabha.
Lawmaker’s Privileges in India
Lawmakers in India, including Members of Parliament (MPs) and Members of Legislative Assemblies (MLAs), have specific privileges to ensure they can perform their duties effectively. These privileges include:
- Protection Against Misinformation: Lawmakers are safeguarded against false information within the legislative House.
- Speech Immunity: Speeches made by lawmakers in the House cannot be challenged in court.
- Right to Reply: Lawmakers have the right to respond if they are mentioned by another member.
- Prior Information: Lawmakers must be informed about any government policy or law changes during a legislative session before they are made public.
What Constitutes a Breach of Privilege?
- A breach of privilege occurs when:
- Unsubstantiated Comments: An unsubstantiated comment is made against a member or minister.
- Maligned Reputation: The reputation of an MP is damaged.
- Obstruction of Duties: A lawmaker is hindered from performing their duties.
- In such cases, the affected lawmaker can file a complaint to the Speaker (or the Chairman in the case of Rajya Sabha) claiming that their privileges have been breached.
- Once a breach of privilege notice is moved, the Speaker examines its feasibility.
- Referral to Committee: If the Speaker consents, the notice is sent to the privileges committee for detailed examination.
- Committee Review: The committee calls both the accused and the complainant before submitting its report to the House.
- Further Action: The House decides on the necessary action based on the committee's report.
Fact Box: Rules Governing Privilege Notices in India
|


Prelims Articles
Context
A new project has been launched to accelerate the development and availability of H5N1 avian influenza mRNA vaccines for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
About
- H5N1 is a subtype of the influenza virus that primarily affects birds but can infect humans and other animals.
- It poses a significant risk due to its potential to cause a future pandemic.
- mRNA Vaccines:
- Mechanism: mRNA vaccines use messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response without using a live virus.
- They can be developed and produced faster than traditional vaccines.


Prelims Articles
Context
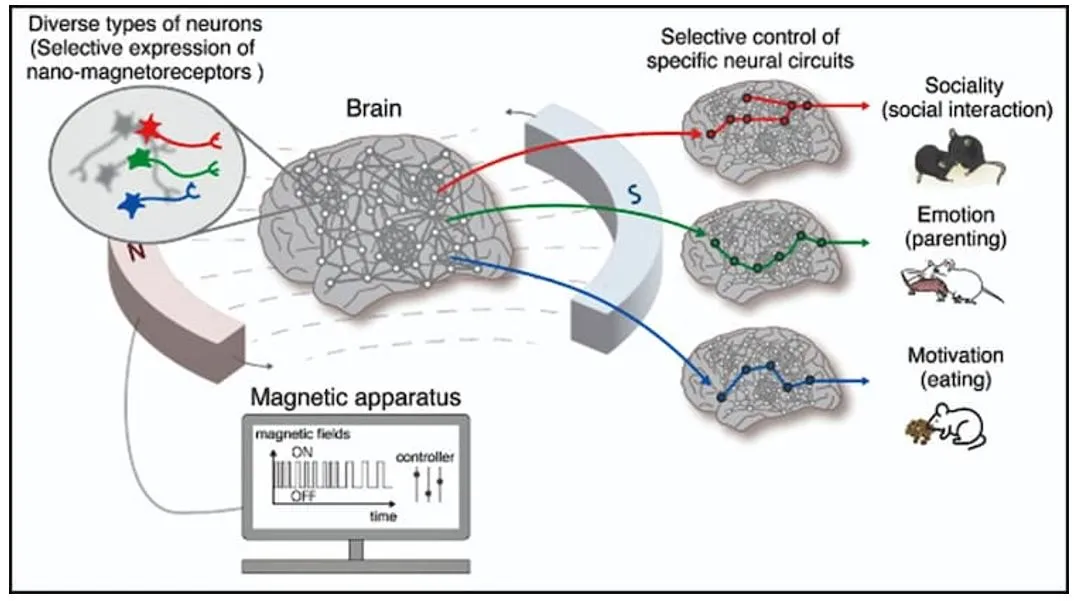
Researchers have achieved a world-first by using magnetic fields to control specific brain regions in mice. This breakthrough technology is called Nano-MIND (Magnetogenetic Interface for NeuroDynamics).
Key Points:
- This breakthrough is known as Nano-MIND (Magnetogenetic Interface for NeuroDynamics) technology.
- It helps in understanding and manipulating complex brain functions such as cognition, emotion, and motivation.
- It enables wireless, remote, and precise control of deep brain neural circuits using magnetic fields and magnetized nanoparticles.
- Applications: It opens new possibilities for understanding and manipulating complex brain functions such as cognition, emotion, and motivation.
- Significance:
- Precision: The technology provides precise modulation of specific brain regions, enhancing the study of brain functions.
- Non-Invasive: Nano-MIND allows for remote control without the need for invasive procedures, making it a safer and more effective method for brain research.


Editorials
Context
Kerala is facing severe floods and landslides, especially in districts like Wayanad, exacerbated by heavy rains and the opening of dam shutters. This has led to significant damage to homes, livelihoods, and infrastructure, highlighting the ongoing struggle with natural disasters and the need for improved environmental policies.
The Situation in Kerala:
- Recurring Floods: Since 2018, annual monsoons have led to frequent flooding in Kerala, causing extensive damage to homes and belongings.
- Landslide Statistics: Kerala reported the highest number of landslides in India between 2015 and 2022, with major landslides in Wayanad in 2024 wiping out entire villages.
- Impact on Communities: The continuous natural disasters have led to a constant state of preparedness and anxiety among Keralites, with significant losses in peace and safety.
Environmental Policies and Challenges:
- Gadgil Committee Report: The Madhav Gadgil Committee (2011) recommended designating ecologically sensitive areas in Kerala to prevent environmental degradation.
- Resistance to Recommendations: Protests erupted against the committee's recommendations, especially among farmers fearing eviction, leading to a halt in policy implementation.
- Need for Inclusive Conservation: Effective environmental conservation requires involving local communities and balancing ecological needs with development and livelihoods.
Mains Question:
Q. The recurring natural disasters in Kerala, such as floods and landslides, highlight the urgent need for integrating environmental conservation with community involvement. In this context, evaluate the effectiveness of the Gadgil Committee's recommendations and suggest how environmental policies can be made more inclusive and sustainable.


Editorials
Context
The fiscal health and debt management of Indian states vary significantly, despite common constitutional rules on borrowing. The 16th Finance Commission's recommendations will shape state fiscal deficits from 2026-2027 to 2030-31.
Trends in State Borrowing:
- Shift to Market Borrowings: Since 2006-07, states have relied more on market borrowings than loans from the Centre, with borrowings surging to Rs 10.1 trillion in 2023-24.
- Debt Redemption: The stock of state government securities (SGS) outstanding was estimated at Rs 56.5 trillion by March 2024, with significant redemption due between 2025-30, led by states like Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Tenor Variation: States have shown variation in the tenor of borrowings, with some preferring shorter tenors and others opting for longer-term securities, affecting their rollover risk.
Risks and New Loan Forms:
- Rollover Risk: The weighted average maturity of SGS has increased, reducing near-term rollover risk, with some states borrowing more in longer-tenor segments.
- Pandemic-Induced Loans: New loans from the Centre emerged during the pandemic, including GST compensation loans and 50-year interest-free loans, impacting the overall debt profile.
- Impact on State Resources: The interest-free capex loan scheme from the Centre, which has significantly increased, will influence state resources for capital spending and their market borrowing needs.
Mains Question:
Considering the variations in fiscal outcomes and debt management across Indian states, critically evaluate the effectiveness of market borrowings as a primary source of funding for state governments. How do the pandemic-induced loan schemes influence state-level fiscal policies and debt sustainability?


Editorials
Context
The Indian government, through an office memorandum dated June 3, has outlined new guidelines for arbitration and mediation in domestic public procurement contracts, signaling a shift away from arbitration towards traditional court litigation. This change will significantly impact the legal system and economic environment.
Impact of Shifting from Arbitration:
- Increased Court Burden: The move away from arbitration will add significant pressure on an already overburdened legal system, leading to delays and increased court interference.
- Negative Repercussions: The decision will adversely affect private litigants, India's "Ease of Doing Business" ranking, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), and overall legal system efficiency.
- Litigation Process: The appeals process will become more extensive, potentially reaching the Supreme Court frequently due to government involvement, prolonging dispute resolution.
Concerns and Future Prospects:
- Historical Reforms: The 2015 amendments aimed to establish India as an arbitration hub, but subsequent amendments and the 2024 memorandum have reversed these gains, citing quick resolution as an issue.
- Quality of Representation: Arbitrations are often lost due to poor legal representation rather than corrupt arbitrators; solutions should focus on accreditation and training.
- Commercial Court Litigation: While arbitration diminishes, an increase in commercial court litigation may develop robust jurisprudence and demand for skilled trial lawyers, strengthening the legal ecosystem, albeit requiring substantial government investment.
Mains Question:
Q. In light of the recent shift away from arbitration in government contracts, critically assess the impact on India's legal and economic environment. Discuss whether increased commercial court litigation can offset the negative consequences of this shift.





