Centre in final stages of notifying emissions trading scheme
Context
After the passing of the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill last December, the Centre is now in the final stages of notifying an Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) that would require polluting industries to achieve certain standards of energy efficiency and permit them to ‘trade’ these improvements.
About
What is Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS)?
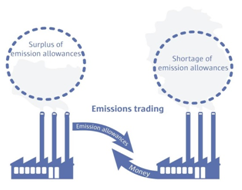
- Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) missions trading is a market-based approach to control pollution.
|
Kyoto Protocol:
|
- By creating tradable pollution permits it attempts to add the profit motive as an incentive for good performance.
- The main form of emissions trading is known as “cap and trade“:
- acap on emissions is set and then permits are created up to the level of this cap.
- The companies or other entities covered by the scheme need to hold one permit for every tonne of pollution (CO2e) they emit.
- Allowing a trade in these permits puts a price on pollution – the cost of emitting one tonne of carbon dioxide is the cost of the permit – and creates flexibility as to how and where pollution is reduced.
- Emissions trading is a central element of the Kyoto protocol in the form of the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM).
Why is it preferred?
- This is preferable to other forms of pricing, such as carbon taxes, which do not guarantee any particular level of reduction.
Criticism:
- Criticism is that emission trading has been marred by weak caps, free handouts of permits to the biggest polluters and the purchase of “offsets” – carbon credits bought from outside the cap-and-trade system from carbon reduction projects in the developing world.