

|
Overview
|
Context
Scientists have mapped out more than a million cells across 33 organs in the human body. The map can help to provide unparalleled insights into health and diseases.
Background
- The Human Cell Atlas is a project to describe all cell types in the human body.
- The initiative was announced by a consortium after its inaugural meeting in London in October 2016.
- In October 2017, the Chan Zuckerberg’s Initiative announced funding for 38 projects related to the Human Cell Atlas.
- By April 2018, the project included more than 480 researchers conducting 185 projects.
- In April 2018, the first data set from the project was released, representing 530,000 immune system cells collected from bone marrow and cord blood.
Analysis
What is a Human Cell Atlas?
- The Human Cell Atlas will be catalogue of a cell based on several criteria,
- The cell type
- Its state
- its location in the body
- The transitions it undergoes
- The lineage of the cell
- It will gather data from existing research, and integrate it with data collected in future research projects.
- Its scope is to categorize the 37 trillion cells of the human body to determine which genes in each cell expresses the sampling cells from all parts of the body.
- All aspects of the project will be made "available to the public for free", including software and results.
Key features
- The HCA aims to identify and describe every cell type in the human body.
- Two main approaches to achieve this will be scRNAseq and spatially resolved methods.
- Sources of human tissue samples and appropriate handling techniques will be key to this project.
- Many single-cell sequencing approaches exist and so the HCA has the opportunity to perform systematic comparisons as well as to develop novel methods.
- Single-cell sequencing data present unique computations challenges and rich areas for innovation.
|
The scRNA-seq technique
|
What does it aim?
- The initiative can transform our understanding of the trillions of cells in the human body.
- Without maps of different cell types, their molecular features and location in the body, we cannot describe all their functions or understand the networks that direct their activities.
- The map can also help us understand how a disease emerged in a body and identify the precise place or cell where it arises.
- It will allow us to develop more precise diagnostics for patients and new treatments.
How does it collect data?
- Steps involved:
- The exact approach that will be taken to build the HCA remains under discussion.
- The current state-of-the-art of technical approaches that could be used to generate the Atlas are in three areas;
- Sample acquisition, data-generating technologies and computational analyses.
- Sample acquisition: obtaining samples from all the tissues that are present in a human is the initial challenge for human cell atlas.
- The single-cell resolution that will be a defining feature of the HCA were able to fix, freeze or analyse tissues immediately after collection and then ship the samples to central facilities for gene expression assays.
- Data-generating technologies: Once tissue samples have been acquired, they must be analysed to determine the cell populations contained within.
- The choice of platforms and protocols used within the HCA will depend on balancing requirements of throughput, data quality and cost.
- A key driver of the rapid growth in single-cell research has been the commercial availability of instruments that partition and process cells for scRNAseq analysis.
- The first of its kind was Fluidigm’s C1 platform, which captures cells at low to medium throughput using a microfluidic circuit, where the cells are lysed and reverse transcribed, and cDNA is amplified.
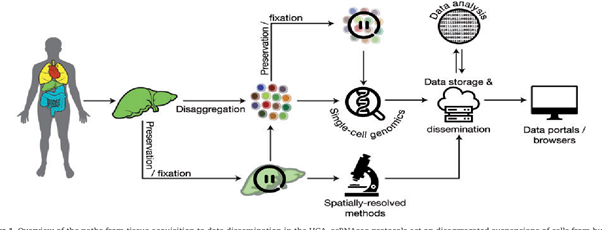
- Computational analyses: The computational process can be split into four broad areas:
- Estimation of expression levels,
- Definition of cell identity,
- Identification of gene signatures and
- Analysis of spatially resolved data.
Global Initiatives
- India’s Project’ MANAV’
- The project named ‘Manav’ has been launched by the Department of Biotechnology and Persistent Systems, a biotechnology company.
- This mega project will collate and integrate molecular information on human tissues and organs that currently lies hidden in research articles in an unstructured and disorganized form.
- Human Genome project: The Human Genome Project originally aimed to map the nucleotides contained in a human haploid reference genome (more than three billion).
- The "genome" of any given individual is unique; mapping the "human genome" involved sequencing a small number of individuals and then assembling to get a complete sequence for each chromosome.
- Therefore, the finished human genome is a mosaic, not representing any one individual. The utility of the project comes from the fact that the vast majority of the human genome is the same in all humans.
- The Human Protein Atlas(HPA): is a Swedish-based program started in 2003 with the aim to map all the human proteins in cells, tissues and organs using integration of various omics technologies, including antibody-based imaging, mass spectrometry-based proteomics, transcriptomics and systems biology.
- All the data in the knowledge resource is open access to allow scientists both in academia and industry to freely access the data for exploration of the human proteome.
Benefits
- Biological scope: The full atlas, will ultimately describe at least 10 billion cells, covering all tissues, organs, and systems. Specimens will come from both healthy research participants and small cohorts of patients with relevant diseases.
- Model organisms: The Human Genome Project and the broader scientific community benefitted from insights learned from genome projects conducted in parallel in model organisms. These projects empowered functional studies in model organisms, ushered a new era of comparative genomics, and provided important technical lessons.
- Open data availability: The Human Genome Project made clear the power of open data that can be used by all and freely combined with other datasets. A Human Cell Atlas should similarly be an open endeavor, to the full extent permitted by participants' wishes and legal regulation.
- Helps scientific community: it will provide the core scientific knowledge and discoveries that will result from having a reference map;
- the empowerment of scientists working across any tissue or cell type to pursue their research more precisely and effectively;
- the development, hardening and dissemination of experimental techniques and computational methods in the context of big-data settings,
- all of which will be openly shared; the inclusive and maximally open Human Cell Atlas community,
- inviting participation by all individual labs and research centers; and
- The coordination of efforts that would otherwise be unconnected, less extensive, and more expensive.
Concerns
- Lack of global equity: Geographical atlases of the Earth were largely developed to serve global power centers. The Human Cell Atlas should be designed to serve all people. it should span genders, ethnicities, environments, and the global burden of diseases –all of which are likely to affect the molecular profiles of cells and must be characterized to maximize the atlas's benefits.
- Problem to scientists: They may face premature restriction to specific technologies or approaches, which might limit innovation in a fast-moving field, implicit restriction of participation, based on available resources; and diversion of funding from other research directions.
- Lack of non-governmental cooperation: The general public is a key stakeholder community for the Human Cell Atlas. Proper public engagement should involve many communities, including interested members of the public, citizen-scientists, schoolchildren, teachers and, where appropriate, research participants. Engagement will take diverse forms, including traditional media, social media, video and, importantly, direct sharing of the project's data.
Conclusion
Conclusion
The past quarter-century has many times showed the value of the scientific community joining together in collaborative efforts to generate and make freely available systematic information resources to accelerate scientific and medical progress in tens of thousands of laboratories around the world. The Human Cell Atlas builds on this rich tradition, extending it to the fundamental unit of biological organization: the cell. Many challenges will arise along the way, but we are confident that they can be met through scientific creativity and collaboration.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q1. What is human cell atlas? Discuss its significance in medical field. Q2. What are the applications of genome sequencing in healthcare? Discuss the associated challenges with respect to genome sequencing in India. |


