Context
The United Kingdom slipped into recession, with its worst gross domestic product (GDP) performance in 2023 in years. Japan lost its spot as the world’s third-largest economy. Its economy is now the world’s fourth-largest after it contracted in the last quarter of 2023 and fell behind Germany.
What is a Recession?
- A recession is commonly defined as two consecutive quarters of contraction.
- A recession is a significant decline in economic activity that lasts for months or even years.
- Experts declare a recession when a nation’s economy experiences
- negative gross domestic product (GDP)
- rising levels of unemployment
- falling retail sales
- contracting measures of income and manufacturing for an extended period of time
What causes recessions?
These phenomena are some of the main drivers of a recession:
- A sudden economic shock: An economic shock is a surprise problem that creates serious financial damage.
- Excessive debt: When individuals or businesses take on too much debt, the cost of servicing the debt can grow to the point where they can’t pay their bills.
- Asset bubbles: When investing decisions are driven by emotion, bad economic outcomes aren’t far behind.
- Too much inflation: Inflation is the steady, upward trend in prices over time.
- Too much deflation: While runaway inflation can create a recession, deflationcan be even worse.
Why UK, Japan fell into recession?
|
United Kingdom |
Japan |
|
The UK economy fell into recession at the end of last year as hard-pressed households cut back on spending amid the cost of living crisis
|
A weaker Japanese yen was a key factor in the drop to fourth place, since comparisons of nominal GDP are in dollar terms. But Japan’s relative weakness also reflects a decline in its population and lagging productivity and competitiveness. |
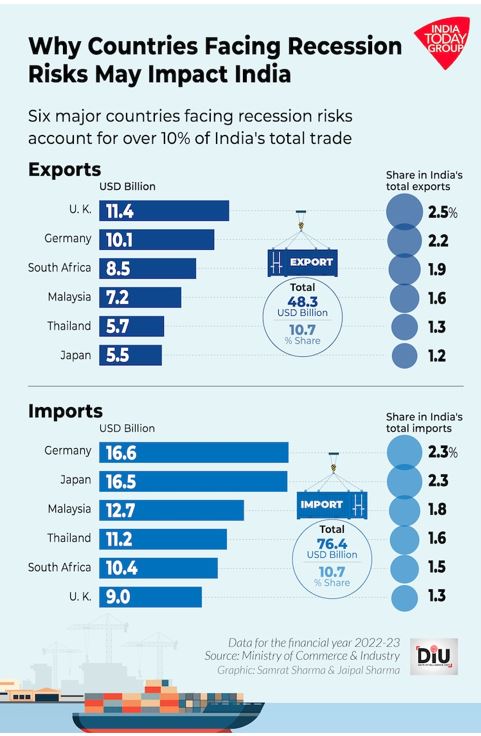
How would it impact India?
- While India’s GDP has been performing relatively better, no one is immune to economic problems, in the era of globalisation.
- External headwinds are poised to hurt India’s economy too, as service exports are a major part of revenue generated by India’s IT industry and global price rise can make India’s imports expensive.
- India & the UK:Negotiations between India and the United Kingdom for the proposed free trade agreement (FTA) are at an advanced stage, but India is keen to safeguard its interests.
- India & Japan:According to the MEA’s October 2023 report, bilateral trade totaled US$ 21.96 billion during FY 2022- 23. Exports from Japan to India during this period were US$ 16.49 billion and imports were US$ 5.46 billion.
What is India’s future prospective?
- Shrinking gap: The gap between developed countries and emerging nations is shrinking, with India likely to overtake Japan in nominal GDP in a few years.
- India is likely to overtake Japan to become the world’s third-largest economy with a GDP of USD 7.3 trillion by 2030, S&P Global Market Intelligence said in its issue of PMI in October 2023.
- Beneficial diversification: India is benefiting from growing interest from multinationals, which see the country as a key alternative manufacturing base in the context of developed economies' supply chain diversification strategies.
What India can do to sidestep the recessionary trend?
- India is currently the world's fifth-largest economy, placed behind the US, China, Japan and Germany.
- For India, it's crucial to continue focusing on-
- strengthening domestic demand
- enhancing productivity
- promoting sectors with high growth potential
- diversifying trade partners
- reducing dependency on a single market for exports and imports